MCQ ON Sporulation (Asexual Reproduction) for NEET |MCQ ON —NEET Biology class 12th |MCQ Questions for class 12 Biology chapter 1, Sporulation (Asexual Reproduction) with answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 12 Biology chapter 1 based on Sporulation (Asexual Reproduction) with answers.
MCQ Questions for class 12 Biology with Answers were prepared based on the latest pattern. We have provided class 12 Biology MCQs questions on Sporulation (Asexual Reproduction) with answers to help students understand the concept very well.
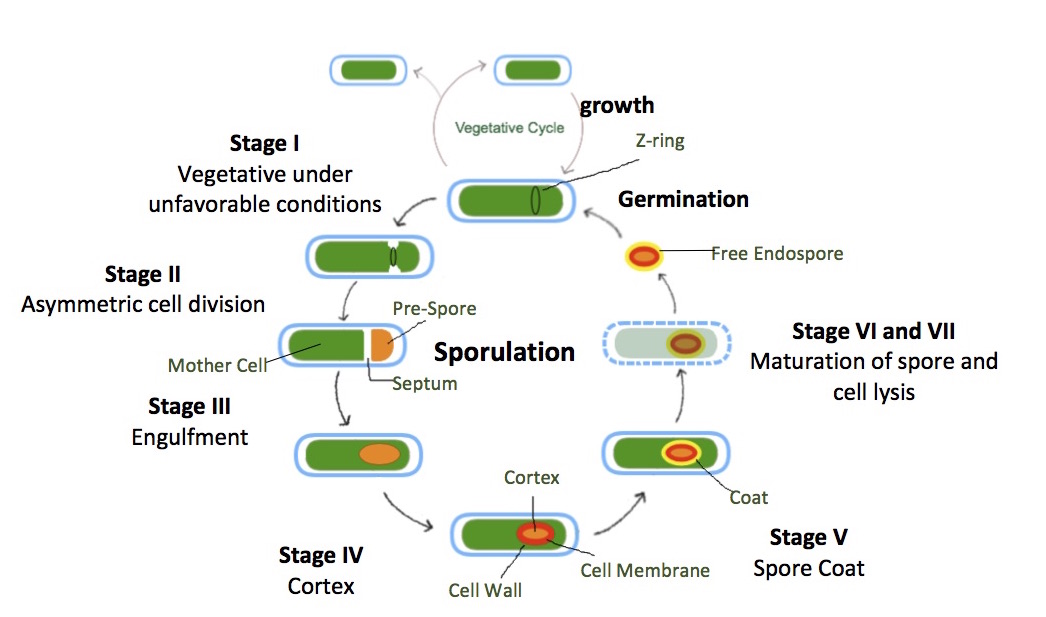
Sporulation (Asexual Reproduction)
MCQ on is useful for NEET/ CSIR/ UGC/ CBSE/ ICSE /AIIMS EXAM/ AFMC EXAM/ JAC exam/ STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM
Introduction:-
Sporulation:- Sporulation is a biological process in which certain organisms, such as bacteria, fungi, algae, and some protozoa, produce specialized reproductive cells called spores. These spores are highly resistant and are adapted to survive harsh environmental conditions, allowing the organism to disperse and potentially give rise to new individuals when conditions become favorable.
Key points about sporulation:
1.Formation of Spores: During sporulation, an organism undergoes a series of developmental changes to produce spores. These spores are typically enclosed by a protective outer layer, which helps shield them from adverse conditions.
2.Resistance: Spores are highly resistant to desiccation (drying out), temperature extremes, radiation, and chemicals. This resistance allows spores to survive in environments where the parent organism might not.
3.Dispersal: Spores are often dispersed by various means, such as wind, water, or animal vectors. This dispersal mechanism helps spores reach new locations where they may germinate and develop into new individuals under more favorable conditions.
4.Asexual Reproduction: Sporulation is a form of asexual reproduction because the spores produced are genetically identical to the parent organism. However, spore formation is not limited to asexual reproduction, as some organisms also produce spores as part of their sexual reproduction cycle.
Examples of sporulation include:
Bacterial Sporulation: Certain types of bacteria, such as Clostridium and Bacillus species, form endospores. These endospores are highly resistant and can survive in extreme conditions. They can return to their vegetative state and multiply when conditions improve.
Fungal Sporulation: Fungi, including molds and yeast, produce spores as part of their reproductive cycle. These spores can be produced both sexually and asexually, depending on the fungal species.
Algal Sporulation: Some types of algae, particularly green algae, form reproductive spores that can disperse in water and give rise to new algal colonies.
Sporulation is an important adaptation that allows organisms to endure adverse conditions and ensure their survival and reproduction when circumstances become more favorable.
MCQ ON Sporulation (Asexual Reproduction)
Here are 10 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) related to the process of Sporulation in asexual reproduction, along with their answers:
1. What is sporulation?
a) A process in which organisms produce reproductive spores
b) A form of sexual reproduction in plants
c) A method of seed dispersal in animals
d) A type of bacterial infection
Answer: a) A process in which organisms produce reproductive spores
2. Which of the following is NOT an organism that can undergo sporulation?
a) Bacteria
b) Fungi
c) Mammals
d) Algae
Answer: c) Mammals
3. What is the primary purpose of spore formation in sporulation?
a) To create genetic diversity
b) To produce offspring with identical genetics
c) To ensure sexual reproduction
d) To allow organisms to disperse and survive harsh conditions
Answer: d) To allow organisms to disperse and survive harsh conditions
4. Which of the following is an example of a highly resistant spore-forming bacterium?
a) E. coli
b) Clostridium botulinum
c) Salmonella
d) Streptococcus
Answer: b) Clostridium botulinum
5. How are bacterial endospores different from typical bacterial cells?
a) Endospores are more sensitive to environmental changes.
b) Endospores are metabolically active.
c) Endospores lack a protective outer layer.
d) Endospores are highly resistant and dormant.
Answer: d) Endospores are highly resistant and dormant.
6. In fungal sporulation, what is the primary function of spores?
a) To produce food for the fungus
b) To facilitate sexual reproduction
c) To allow the fungus to photosynthesize
d) To disperse and form new fungal colonies
Answer: d) To disperse and form new fungal colonies
7. Which of the following is an example of fungal spores commonly used in food production and fermentation?
a) Algae spores
b) Bacterial spores
c) Yeast spores
d) Mold spores
Answer: c) Yeast spores
8. What is the term for the process of spore dispersal by wind or other means?
a) Sporogenesis
b) Sporulation
c) Sporophyte
d) Spore discharge
Answer: d) Spore discharge
9. Which group of organisms often relies on spore formation for both asexual and sexual reproduction?
a) Birds
b) Insects
c) Plants
d) Fungi
Answer: d) Fungi
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
10. What is the primary advantage of sporulation for organisms living in unpredictable environments?
a) It allows for rapid reproduction.
b) It creates genetic diversity.
c) It conserves energy.
d) It provides a means of survival in adverse conditions.
Answer: d) It provides a means of survival in adverse conditions.
Conclusion:-
MCQ ON Sporulation (Asexual Reproduction) for NEET | What is the term for the process of spore dispersal by wind or other means? a) Sporogenesis, b) Sporulation, c) Sporophyte, d) Spore discharge, Answer: d) Spore discharge







Leave a Comment