MCQ ON Budding (Asexual Reproduction) for NEET |MCQ ON —NEET Biology class 12th |MCQ Questions for class 12 Biology chapter 1, Budding (Asexual Reproduction) with answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 12 Biology chapter 1 based on Budding (Asexual Reproduction) with answers.
MCQ Questions for class 12 Biology with Answers were prepared based on the latest pattern. We have provided class 12 Biology MCQs questions on Budding (Asexual Reproduction) with answers to help students understand the concept very well.
MCQ ON Budding (Asexual Reproduction) for NEET
MCQ on is useful for NEET/ CSIR/ UGC/ CBSE/ ICSE /AIIMS EXAM/ AFMC EXAM/ JAC exam/ STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM
Introduction:-
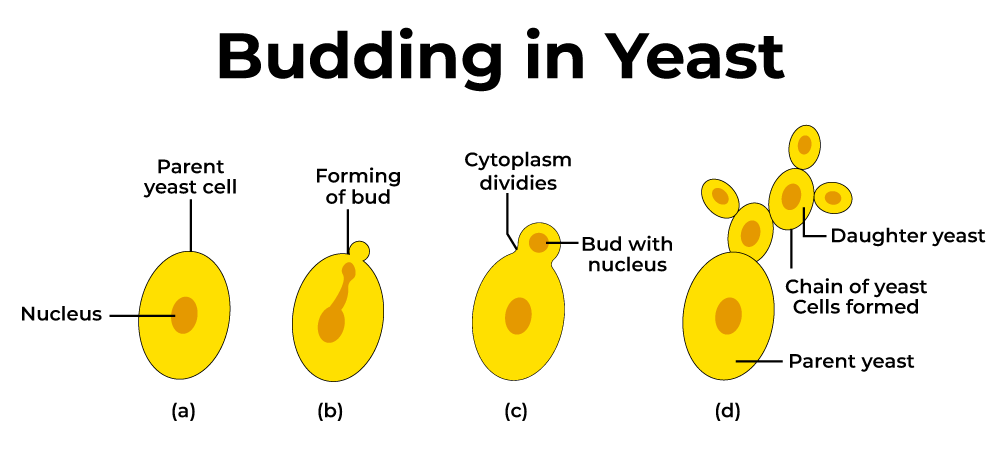
Budding:- Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism, often called a “bud,” develops as an outgrowth or small projection on the body of the parent organism. This bud eventually separates from the parent and grows into a genetically identical individual.
Key points about budding:
1. Process: Budding begins with the formation of a small bulge or bud on the parent organism’s body. This bud contains a portion of the parent’s cells and genetic material.
2. Growth: The bud continues to grow and develop while attached to the parent organism. It may develop into a miniature version of the parent.
3. Separation: Eventually, the bud detaches from the parent organism, either by physical splitting or as a result of environmental conditions. This detached bud becomes an independent organism.
4. Genetic Identity: Budding typically produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent organism. This is because the genetic material of the bud is a copy of the parent’s genetic material.
5. Examples: Budding is commonly observed in various organisms, including simple animals like hydras and some species of corals, as well as in unicellular organisms like yeast.
6. Advantages: Budding is a rapid method of reproduction that does not require the involvement of another organism for fertilization. It can be advantageous in stable environments or when resources are abundant.
7. Variations: There are variations of budding, including internal budding (where the bud forms within the parent’s body) and external budding (where the bud forms on the external surface of the parent).
Budding is a reproductive strategy that allows organisms to efficiently produce offspring under certain conditions, particularly when sexual reproduction may be less practical or necessary.
MCQ ON Budding (Asexual Reproduction) for NEET
Here are 15 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) related to the process of budding in asexual reproduction, along with their answers:
1. What is budding in asexual reproduction?
a) The splitting of an organism into two equal parts
b) The formation of spores for reproduction
c) A process where a new organism grows from an outgrowth on the parent
d) The fusion of two gametes to produce offspring
Answer: c) A process where a new organism grows from an outgrowth on the parent
2. Which of the following organisms commonly reproduce by budding?
a) Fish
b) Mammals
c) Yeast
d) Birds
Answer: c) Yeast
3. In budding, the outgrowth or bud typically develops into which of the following?
a) An entirely new organism
b) A seed
c) A spore
d) An egg
Answer: a) An entirely new organism
4. Where is budding commonly observed in multicellular organisms?
a) In the roots of plants
b) In the leaves of trees
c) In the reproductive organs of animals
d) In the stems of fungi
Answer: c) In the reproductive organs of animals
5. Which part of the parent organism gives rise to the bud in budding?
a) The roots
b) The leaves
c) The stem or body
d) The head
Answer: c) The stem or body
6. During budding, what happens to the nucleus of the parent cell?
a) It divides into two equal parts
b) It migrates into the bud
c) It remains in the parent cell
d) It disintegrates
Answer: c) It remains in the parent cell
7. In which type of environment is budding advantageous for organisms?
a) Highly competitive environments
b) Stable and unchanging environments
c) Environments with abundant resources
d) Aquatic environments
Answer: a) Highly competitive environments
8. Which of the following is an example of an organism that reproduces by external budding?
a) Hydra
b) Bacteria
c) Earthworm
d) Oak tree
Answer: a) Hydra
9. What is the primary advantage of budding as a reproductive strategy?
a) It generates genetic diversity
b) It is a rapid method of reproduction
c) It requires a mate for fertilization
d) It conserves energy
Answer: b) It is a rapid method of reproduction
10. In some cases, budding can lead to the formation of a colony of genetically identical individuals. What is this colony called?
a) A family
b) A community
c) A clone
d) A society
Answer: c) A clone
11. What is the term for the small, detached bud that has the potential to develop into a new organism?
a) Embryo
b) Spore
c) Larva
d) Daughter cell
Answer: a) Embryo
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
12. Which of the following is an advantage of budding over sexual reproduction?
a) Greater genetic diversity
b) Enhanced adaptation to changing environments
c) Lower energy expenditure
d) Longer lifespan
Answer: c) Lower energy expenditure
13. Which group of organisms includes examples of both internal and external budding?
a) Mammals
b) Birds
c) Cnidarians
d) Insects
Answer: c) Cnidarians
14. What triggers the initiation of budding in organisms?
a) Mating with a partner
b) Environmental cues
c) A sudden increase in temperature
d) Exposure to sunlight
Answer: b) Environmental cues
15. Which of the following is NOT a common use of budding in biotechnology?
a) Cloning of organisms
b) Production of bread and beer
c) Treatment of infections
d) Genetic modification of crops
Answer: c) Treatment of infections
Conclusion:-
MCQ ON Budding (Asexual Reproduction) for NEET |Which of the following is an example of an organism that reproduces by external budding? a) Hydra, b) Bacteria, c) Earthworm, d) Oak tree, Answer: a) Hydra.







Leave a Comment