MCQ ON OVULE class 12 for NEET | OVULE class 12 | MCQ OVULE with Answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 12 Biology based on the with Answers.
MCQ ON OVULE class 12 for NEET
MCQ on OVULE class 12 Biology with answers were prepared based on the latest pattern. We have provided class 12 Biology MCQs questions on OVULE with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
MCQ ON OVULE is useful for NEET / CSIR / UGC / CBSE / ICSE / AIIMS / EXAM / AFMC EXAM / STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM 2022-23, 2023-24
Introduction:-
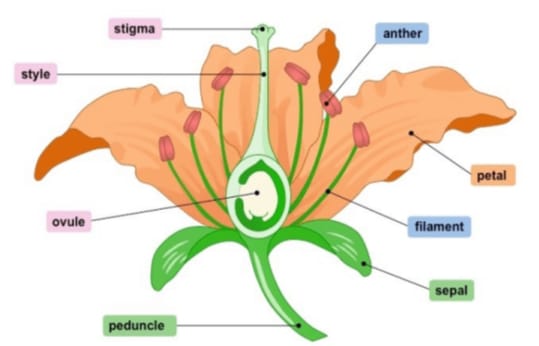
A carpel or pistil has a stigma or receptive region for pollen grains, a stalk or style and basal swollen region or ovary. Ovary contains one to several ovules.
Ovule is integumented indehiscent megasporangium of phanerogams which on fertilization ripens into a seed. It is oval and whitish.
The Ovule is attached to placenta by means of a stalk called funiculus .The point of attachment of funiculus to the ovule is known as hilum.
A raphe is formed by the fusion of funiculus with the body of Ovule.The actual megasporangium equivalent is a parenchymatous tissue called nucellus.It may be thin .
Nucellus is covered by one integument or two integuments.The inner region of integuments may provide nourishment to developing embryo sac when it is called a endothelium.
Outer side of each integument as well as nucellus possess cuticle.
MCQ ON OVULE class 12 for NEET
1. Ovule develops as a merismatic primordium over
(a) placenta
(b) funicle
(c) micropyle
(d) hilum
Ans (a) placenta
2.Ovule first rise to
(a) integument
(b) nucellus
(c) embryo sac
(d) antipodal
Ans. (b) nucellus
3. The body of Ovule live straight and upright over the funicle .Hilum , chalaza and micropyle occur on the same line with hilum and chalaza nearby .
(a) anatropous
(b) orthotropous
(c) hemitropous
(d) amphitropous
Ans. (b) orthotropous
4. The body of Ovule is inverted and gets fused with funiculus along its whole length on one side.
(a) orthotropous
(b) anatropous
(c) amphitropous
(d) campylotropous
Ans.(b) anatropous
5. The body is curved but the embryo sac is straight .Hilum ,chalaza and micropyle come nearby.
(a) campylotropous
(b) anatropous
(c) circinotropous
(d) amphitropous
Ans.(a) campylotropous
6. In angiosperms during development of embryo , the suspensor cell develop from
(a) oospore
(b) integument
(c) endosperm
(d) cotyledon
Ans.(a) oospore
7.The funicle is large and coiled around the ovule.
(a) hemitropous
(b) circinotropous
(c) campylotropous
(d) amphitropous
Ans.(b) circinotropous
8. Both body of Ovule and embryo sac are curved.
(a) amphitropous
(b) anatropous
(c) campylotropous
(d) hemitropous
Ans.(a) amphitropous
9. Which is the only diploid structure in the embryo sac?
(a) secondary nucleus
(b) egg cell
(c) antipodal cell
(d) all the above
Ans. (a) secondary nucleus
10.The fused funiculus forms ridge called
(a) raphe
(b) polar
(c) wheat
(d) all the above
Ans. (a) raphe
11. The chalazal cells are known as
(a) synegids
(b) micropyle
(c) antipodal cells
(d) all the above
Ans.(c) antipodal cells
12. The most common forms of Ovule in angiosperms are
(a) orthotropous
(b) anatropous
(c) hemitropous
(d) all the above
Ans . (b) anatropous
13. In opuntia forms of Ovules found
(a) orthotropous
(b) anatropous
(c) amphitropous
(d) circinotropous
Ans.(d) circinotropous
14. Ovules form
(a) seed
(b) fruit
(c) embryo
(d) all the above
Ans. (a) seed
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
15. Megasporangium is equivalent to
(a) Ovule
(b) embryo sac
(c) fruit
(d) nucellus
Ans.(d) nucellus
16. A non – nutritive structure is
(a) tapetum
(b) endosperm
(c) integument
(d) palisade parenchyma
Ans.(c) integument







Leave a Comment