MCQ ON SPECIATION class 12 for NEET | SPECIATION class 12 | MCQ SPECIATION with Answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 12 Biology based on the with Answers.
MCQ ON SPECIATION class 12 for NEET
MCQ on SPECIATION class 12 Biology with answers were prepared based on the latest pattern.We have provided class 12 Biology MCQs questions on SPECIATION with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
MCQ ON SPECIATION is useful for NEET / CSIR / UGC / CBSE / ICSE / AIIMS / EXAM / AFMC EXAM / STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM 2022-23, 2023-24
Introduction:
Evolutionary biology is the study of history of life forms on earth.To understand the changes in flora and fauna that have occurred over millions of years on earth , we must have an understanding of the context of origin of life , of stars, of earth and indeed universe itself.This is the story of origin of life and evolution of life forms or biodiversity on planet earth in the context of evolution of earth and against the background of evolution of Universe itself. Evolution is revealing of hidden potential ties that bring about an orderly change from one condition to another.Cosmic evolution deals with the sequence of changes that occur in inorganic matter and its evolution.
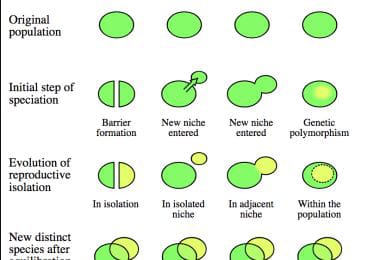
Speciation is the phenomenon of formation of new species from the pre existing once speciation can be a allopatric or sympatric, multiplicative , phyletic, gradual or abrupt.
Allopatric speciation is speciation which occurs due to separation of segment of population from the main population due to distance or geographical barrier cutting across the species range. For example creeping glaciers, development of mountain ,migration of few individual to new habitat away from the original range also causes allopatric speciation.
MCQ ON SPECIATION class 12 for NEET
1. It is the phenomenon of formation of species from the pre existing one
(a) natural selection
(b) mutation
(c) genetic drift
(d) speciation
Ans (d) speciation
2. The type of species in which occurs due to separation of segment of population from the main population due to distance or geographical barrier cutting across the species range.
(a) allopathic speciation
(b) sympatric speciation
(c) peripatric speciation
(d) fusion speciation
Ans. (a) allopatric speciation
3. Darwin’s finches of Galapagos Islands formed 14 different species due to
(a) allopatric speciation
(b) sympatric speciation
(c) natural selection
(d) genetic drift
Ans. (a) allopatric speciation
4. It is speciation that occurs on the periphery of a large population due to separation of small groups bearing unique genotype or gene frequencies
(a) allopatric speciation
(b) peripatric speciation
(c) sympatric speciation
(d) fusion speciation
Ans.(b) peripatric speciation
5. It is speciation which occurs in a subpopulation in the midst of its parent population.
(a) peripatric speciation
(b) sympatric speciation
(c) fusion speciation
(d) rapid speciation
Ans.(b) sympatric speciation
6.It is the autogenous transformation of a species with the passage of time due to piling up of variations.
(a) peripatric speciation
(b) sympatric speciation
(c) fusion speciation
(d) phyletic speciation
Ans.(d) phyletic speciation
7. It is the formation of two or more species from a single species.
(a) cladogenesis
(b) anagenesis
(c) peripatric speciation
(d) ethological isolation
Ans.(a) cladogenesis
8. In large population accumulation of different variations indifferent areas first produces ecotypes then races , varieties , subspecies ultimately different species in an example of
(a) allopatric speciation
(b) adaptive radiation
(c) reproductive is speciation
(d) all the above
Ans.(b) adaptive radiation
9. Two species will interbreed and merge to form single species.
(a) fusion speciation
(b) allopatric speciation
(c) sympatric speciation
(d) phyletic speciation
Ans. (a) fusion speciation
10. Mutations causing genetic isolation forms
(a) sibling species
(b) autopolyploid
(c) allopolyploidy
(d) different species
Ans. (a) sibling species
11. The increase in same chromosome set or genome
(a) autopolyploid
(b) allopolyploidy
(c) adaptive radiation
(d) none of the above
Ans.(a) autopolyploidy
12. Allopatric speciation is usually gradual . Mode of evolution is called
(a) adaptive radiation
(b) divergent evolution
(c) both a and b
(d) Convergent evolution
Ans . (c) both a and b
13. Species inhabiting different geographical areas is known as
(a) allopatric speciation
(b) sympatric speciation
(c) etho species
(d) sibling
Ans.(a) allopatric speciation
14. Evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and its spreading to other geography areas is
(a) migration
(b) natural selection
(c) divergent evolution
(d) adaptive radiation
Ans. (c) divergent evolution
15. Most species originated by an route
(a) allopatric
(b) sympatric
(c) parapatric
(d) parametric
Ans.(a) allopatric
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
16. Evolutionary pattern characterised by increase in number and kind of closely related species is
(a) convergent evolution
(b) parallel evolution
(c) adaptive radiation
(d) divergent evolution
Ans.(c) adaptive radiation
17. A common means of sympatric speciation is
(a) polyploidy
(b) imposition of geographical barrier
(c) spatial segregation of mating sites
(d) formation of similar traits
And.(a) polyploidy
18. Another term for adaptive evolution is
(a) clinical change
(b) microevolution
(c) macroevolution
(d) speciation
Ans. (d) speciation
19. Reproductive isolation between segments of a single population is
(a) sympatry
(b) allopatry
(c) population divergence
(d) disruptive divergence
Ans.(a) sympatry
20. Two species occupying same or overlapping areas are
(a) allopatric
(b) sympatric
(c) parapatric
(d) peripatric
Ans.(b) sympatric







Leave a Comment