MCQ ON PLANT – WATER RELATION class 11for NEET | PLANT – WATER RELATION class 11 | MCQ PLANT WATER RELATION with Answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 11 Biology based on the with Answers.
MCQ on PLANT – WATER RELATION class 11 Biology with answers were prepared based on the latest pattern.We have provided class 11 Biology MCQs question with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
MCQ ON PLANT – WATER RELATION class 11for NEET
MCQ ON PLANT- WATER RELATION is useful for NEET / CSIR / UGC / CBSE / ICSE / AIIMS / EXAM / AFMC EXAM / STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM/ KVS PGT BIOLOGY / NVS PGT BIOLOGY EXAM 2022-2023,2024
INTRODUCTION:-
Water is essential for all physiological activities of the plant and plays a very important role in all living organisms. It provides the medium in which most substances dissolved.
The protoplast of cells nothing but water in which different molecules are dissolved and suspended. A watermelon has 92% of water. A seed may appear dry but it is still has water otherwise it would not be alive and respiring.
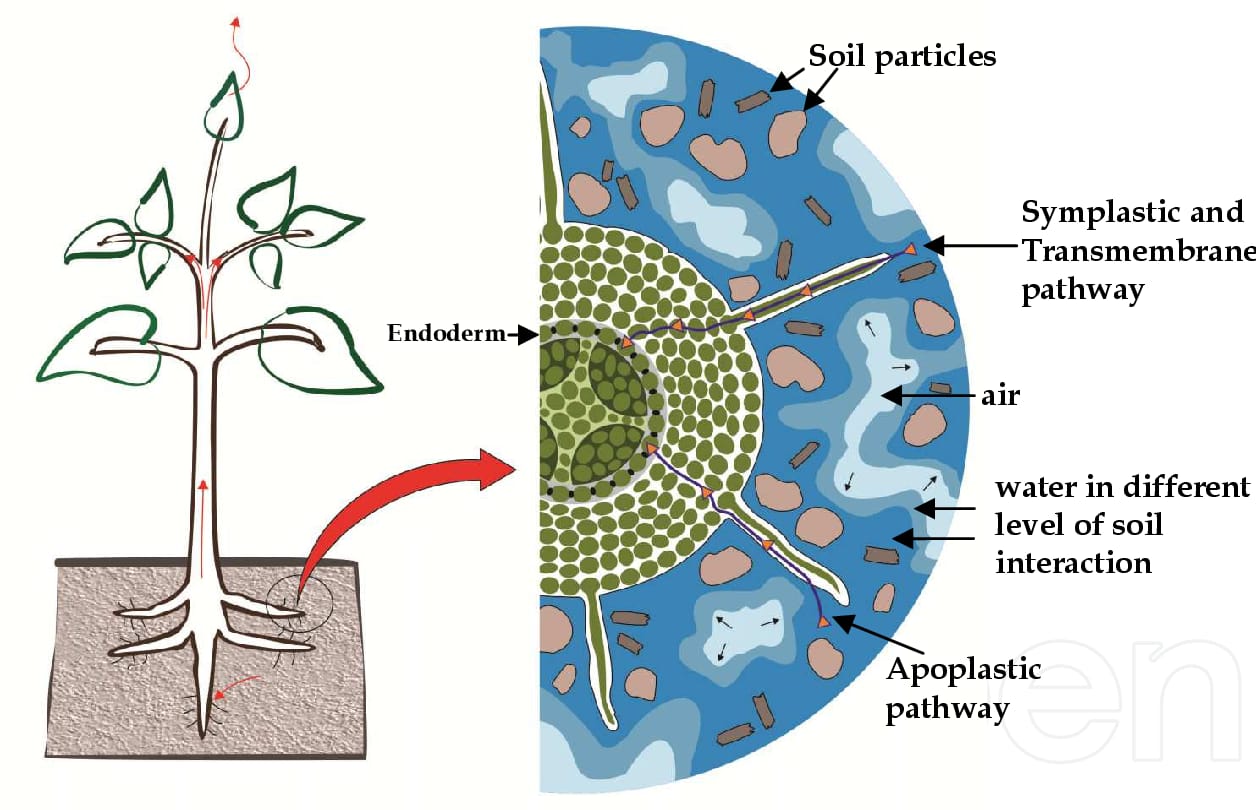
Terrestrial plants take up huge amount water daily but most of it is lost to the air through evaporation from the leaves that is Transpiration.
A mature corn plant observe almost 3 litres of water in a day, while a mustard plant absorbs water equal to its own weigh in about 5 hours.
Water molecule causes kinetic energy. In liquid and gases for they are in random motion that is both rapid and constant. The greater of the concentration of water in a system, the greater is its kinetic energy or water potential. if two systems containing water are in contact random moment of water molecules will result in net movement of water molecules from the system with high energy to the one with lower energy. This process of water will move from the system containing water at higher water potential to the one having low water potential. This process of movement of substances down a gradient of free energy is called diffusion. By convention the water potential of pure water at standard temperature which is not under any pressure is taken to be zero.
Osmosis :-
The plant cell is surrounded by a cell membrane in a cell wall. The cell wall is freely permeable to water and substances in solution hence is not a barrier to movement.
In plants the sales usually contain a large central vacuole whose contents the vacuolar sap , contribute to the solute potential of a cell.
In plant cell the cell membrane and the membrane of the vehicle the tonoplast together important determinants of movement of molecules in or out of the cell.
Osmosis is the term is to refer specifically to the diffusion of water across a differentially or semipermeable membrane. Osmosis occurs spontaneously In response to a driving force. The net direction and rate of osmosis depends on the boards the pressure gradient and concentration gradient.
Water will move from it’s reason of higher chemical potential or concentration to its region of lower chemical potential until equilibrium is reached. At equilibrium the two chambers should have the same water potential.
Lat us discuss experiment where a solution of sucrose in water taken in a funnel is separated from pure water in a beaker through a semi permeable membrane.
You can get this kind of a membrane in an egg.
Remove the yolk and albumin through a small hole at one end of the egg and place of the shell in dilute solution of hydrochloride acid for a few hours.
The egg shell dissolves leaving the membrane intact.This will continue till the equilibrium is reached.
In case sucrose does diffuse out through the membrane , will this equilibrium be ever reached.
External pressure can be applied from the upper part of the funnel through the membrane.This pressure required to prevent water from diffusing is in fact, the osmotic pressure and this is the function of the solute concentration , more the solute concentration , greater will be the pressure to prevent water from diffusing in.
Numerically osmotic pressure is equivalent to the osmotic potential , but the sign is opposite . Osmotic pressure is the positive pressure applied while osmotic potential is negative.
MCQ THE PLANT – WATER RELATION class 12 for NEET/KVS PGT BIOLOGY / NVS PGT BIOLOGY EXAM 2022-2023,2024
1.Terrestrial plants take up huge amount water daily but most of it is lost to the air through evaporation from the leaves.
(a) Diffusion
(b) Osmosis
(c) Hypotonic solution
(d) transpiration
Ans (d) transpiration
2. The two main components that determine water potential .
(a) solute potential
(b) pressure potential
(c) both a and b
(d) osmosis potential
Ans. (c) both a and b
3. The cohesive force existing between molecules of water is contributing to
(a) plasmolysis
(b) translocation
(c) ascent of sap
(d) Osmosis
Ans. (c) ascent of sap
4. Opening and closing of stomata is due to the
(a) hormonal change in guard cells
(b) Change in turgor pressure of guard cells
(c) Gaseous exchange
(d) Respiration
Ans.(b) Change in turgor pressure of guard cells
5. The water potential and osmotic potential of pure water are
(a) 100 and zero
(b) zero and zero
(c) 100 and zero
(d) all the above
Ans.(b) zero and zero
6. Plants will undergo wilting under one of these conditions
(a) high temperatures
(b) high humidity
(c) heavy rainfall
(d) absorption of water
Ans.(a) high temperatures
7. The cause of guttation is mainly
(a) Root pressure
(b) Osmosis
(c) Transpiration pull
(d) Cohesive force
Ans.(a) root pressure
8. Molecules moves inside and outside of living cells by
(a) osmosis only
(b) diffusion only
(c) Osmosis and diffusion
(d) none of the above
Ans.(c) osmosis and diffusion
9. Dixon and Jolly are associated with
(a) light reaction of photosynthesis
(b) anaerobic respiration
(c) cohesion theory of ascent of sap
(d) apical dominance
Ans. (c) Cohesion theory of ascent of sap
10. The real force responsible for the movement of water from one cell to other cell is mainly through
(a) osmetic pressure
(b) Turgor pressure
(c) D.P.D.
(d) Inbibition
Ans. (c) D.P.D
11. Turgor pressure becomes equal to the wall pressure when
(a) water leaves the cell
(b) no exchange of water takes place
(c) water enters the cell
(d) solute goes from the cell into water.
Ans.(b) No exchange of water takes place
12. Cells becomes turgid when placed in
a) isotonic solution
b) hypertonic solution
c) hypotonic solution
(d) all of these
Ans . (c) hypotonic solution
13.In soil , water available for plant is
(a) gravitational water
(b) hygroscopic water
(c) capillary water
(d) chemically bound water
Ans.(c) capillary water
14. plant cells submerged in distil water will become
(a) turgid
(b) flacid
(c) plasmolysed
(d) Impermeable
Ans. (a) turgid
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
15. Water in plants is transported by
(a) cambium
(b) phloem
(c) epidermis
(d) xylem or xylem vessels elements
Ans.(d) xylem or xylem vessels elements
16. guard cells differ from epidermal cells in having
(a) nucleus
(b) mitochondria
(c) ribosomes
(d) chloroplasts
Ans.(d) chloroplasts







Leave a Comment