What are the difference between homologous and analogous organ | definition and example of analogous organ | definition and example of homologous organ | how do you compare homologous from analogous | how do you distinguish homologous from analogous.
What are the difference between homologous and analogous organ
Morphological evidence are the proofs of inter relationship between living organism of different groups which are based on the comparative studies of external and internal morphological structure of different organism these are of following types:- 1) homologous organ and 2) analogous organs.
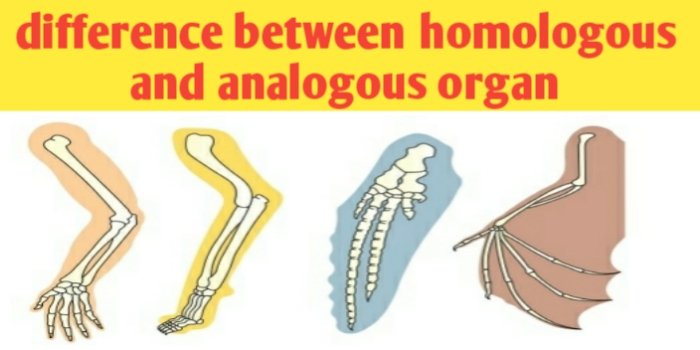
The structures which have similar anatomy, similar basic structure and developmental origin, but different in appearance and perform different functions are said to be homologous organs whereas the structure which have similar appearance, perform similar function but have dissimilar anatomy and dissimilar basic structure and developmental origin are said to be analogous organs.
How do you compare homologous structure from analogous?, when you compare homologous structure from analogous, homologous organ have similar anatomy and similar basic structure and developmental origin but different in appearance and perform different functions whereas analogous structure which have similar appearance, perform similar function but have dissimilar anatomy and dissimilar basic structure and developmental origin.
How do you distinguish homologous from analogous?, there are two main difference that you can distinguish homologous from analogous are, 1) homologous structure have similar anatomy and similar perform basic structure whereas analogous structure have dissimilar anatomy and dissimilar perform basic structure, and 2) homologous structure are result of divergent evolution whereas analogous structure are result of convergent evolution.
How does homologous structure differ from analogous structure?, homologous structure differ from analogous structure in following points- 1) homologous structure have similar anatomy whereas analogous structures have dissimilar anatomy, 2) homologous structure are result of divergent evolution while analogous structure are result of convergent evolution, and 3) homologous structure developed in related species whereas analogous structure developed in unrelated Species.
Homologous organs definition and examples
Homologous structures define as the structure which are different in appearance and perform different function but have similar basic structure and developmental origins are known as homologous organs. For examples arm of a human, the leg of a dog and flipper of a whale are homologous structure.
You can also click on the given link to see others topic in our website and YouTube channels
● Purines and Pyrimidine compare
◆you should also visits our website https://biologysir.com and other website for civil engineer calculation at civilsir.com
■ follow on YouTube
Table of Contents
Characteristics of homologous organs
1) homologous organ is also known as divergent evolution because of same structure have become different in different organism due to different adaptation
2) these structures have different in appearance and different function
3) these structure have similar basic structure and developmental origin
4) the relationship between the structure having common basic plan and similar developmental origin is known as Homology
Example of homologous organs
Examples of homologous organs are following- 1) fore Limb in vertebrate :- four Limbs of vertebrates like birds, seals, bat, horse, men etc are looking different and perform different function but have similar developmental origin and shows similar arrangement of bones blood vessels muscles nerve, 2) comparative anatomy of heart of vertebrate, 3) legs of insects, 4) mouthparts of insects, 5) thorn of bougainvillea and tendril of passiflora, and 6) phylloclad of Opuntia and cladode of Ruscus
Analogous organ definition and examples
Analogous structure or organ defined as those structure which are different in their basic structure and developmental origin but appear similar and perform similar function are known as analogous structure. For examples wings in birds, bats and insects and fins in Penguin and fishes all are analogous structure.
Analogy or convergent evolution definition :- the relationship between a structure of different groups of animals of separate lineage due to their similar function is known as analogy or convergent evolution.
Characteristics of analogous organs
1) these organs have different developmental origin
2) these organs have different basic structure
3) these organs having similar functions and their appearance is similar
4) this lead to convergent evolution or parallel evolution
5) study of analogous organ is known as an analogy
Examples of analogous organs
Examples of analogous structure or organs are following- 1) insects and Bird wing :- these are different in basic and anatomical framework and origin, 2) trachea of insects and lungs of vertebrates, 3) eye of cephalopod and eye of mammals, 4) leaf of plant and cladode of ruscus, and 5) sweet potato and potato tuber
What is the difference between homologous and analogous organ
This questions is very important for class 8th, 9th, 10th, 11th and 12th students those prepared for annual board and others competitive examination
Regarding this, “what is the difference between homologous and analogous structure”, homologous structures have similar anatomy, basic pattern and developmental origin, but different in appearance and function and it is result of divergent evolution whereas analogous structure have dissimilar anatomy and developmental origin but have same appearance and function and it is a result of convergent evolution.
The list of 5 main difference between homologous and analogous structure/ Homologous vs analogous/ differentiate between homologous and analogous structure are following:-
1) homologous organs adapted for different functions but analogous organ adapted for similar functions
2) homologous organs have basic plan and origin but analogous organs have different basic plan and origin
3) homologous organs have divergent evolution but analogous organ have convergent or parallel evolution
4) homology indicates evolutionary relationship but analogy do not indicate evolutionary relationship
5) fore Limbs of vertebrate is an examples of homologous organs and Wings of insects and bird is an example of analogous organ
Important features of homologous and analogous structure
Homologous structure:-
● it has similar anatomy basic pattern and developmental origin
● it appears difference and have dissimilar functions
● it is inherited from common ancestors
● it is developed in related species as a result of divergent evolution
● it is developed as result of the adaptation to a different environment condition
● arm of a human, the leg of a cow or flipper of a whale all are homologous structure
Analogous structure:-
● it has dissimilar anatomy and developmental origin
● their structure appearance is similar and have similar functions
● it is not inherited from ancestors
● it is developed in unrelated species due to result of convergent evolution
● this structure developed as a result of the adaptation to a similar environment condition
● Wings in birds, bats and insects and fins in Penguin and fishes all are analogous structure.
■A) multiple choice questions related with difference between homologous and analogous organ
1) which of following shows divergent evolution
A) analogy
B) homology
C) connecting link
D) vestigial organs
Ans. B
2) which of following shows convergent evolution
A) analogy
B) homology
C) connecting link
D) vestigial organs
Ans. A
3) which organs have not indicate evolutionary relationship
A) analogy
B) homology
C) connecting link
D) vestigial organs
Ans. A
4) which evolution is caused due to adaptive radiation
A) analogy
B) homology
C) connecting link
D) vestigial organs
Ans. B

What are the difference between homologous and analogous organ
5) which one is not an example of homologous organ
A) foreLimbs of vertebrates
B) legs of insects
C) mouth parts of insects
D) Wings of insects and birds
Ans. D
6) which one is an example of humologous organs
A) wings of birds and insects
B) trachea of insects and lungs of vertebrates
C) foreLimbs of vertebrates
D) all of these
Ans. C
7) thorn of Bougainvillea and tendril of passiflora is
A) homologous organs
B) connecting links
C) analogous organs
D) vestigeal organs
Ans. A
8) phylloclad of Opuntia and cladode of Ruscus is
A) homologous organs
B) connecting links
C) analogous organs
D) vestigeal organs
Ans. A
9) leaf of plant and cladode of Ruscus is
A) homologous organs
B) connecting links
C) analogous organs
D) vestigeal organs
Ans. C
10) which organ adapted for different functions
A) homologous organs
B) connecting links
C) analogous organs
D) vestigeal organs
Ans. A
■ B) short answer type questions
1) write definition of homologous organ
2) write definition of analogous organs
3) write definition of homology
4) write definition of analogy
5) what do you mean by convergent evolution
6) what do you mean by divergent evolution
7) write two examples of homologous organs
8) write two examples of analogous organs
9) what is difference between homologous organ and analogous organ





Leave a Comment