MCQ ON THE DNA FINGERPRINTING class 12 for NEET | DNA FINGERPRINTING class 12 | MCQ DNA FINGERPRINTING with Answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 12 Biology based on the with Answers.
MCQ ON THE DNA FINGERPRINTING class 12 for NEET
MCQ on THE DNA FINGERPRINTING class 12 Biology with answers were prepared based on the latest pattern.We have provided class 12 Biology MCQs questions on DNA FINGERPRINTING with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
MCQ ON DNA FINGERPRINTING is useful for NEET / CSIR / UGC / CBSE / ICSE / AIIMS / EXAM / AFMC EXAM / STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM 2022-23, 2023-24
Introduction:
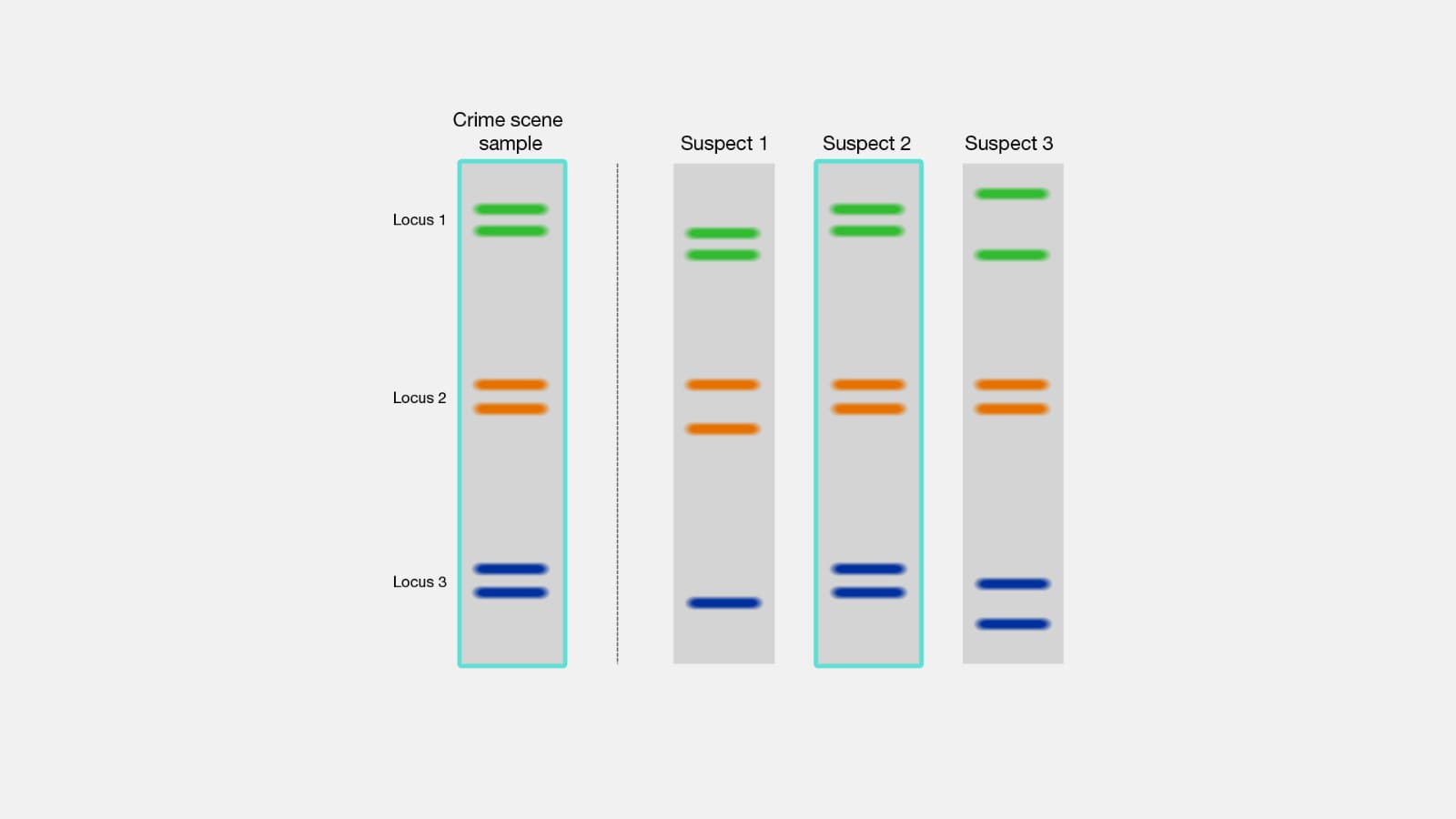
The DNA fingerprint or genetic fingerprinting is the process of analysing VNTR samples of DNA obtained from body fluids or cells so as to establish identity and relation of person. It was a chance discovery by alex jaffrey who was trying to visually identity DNA found between genes in the hope of finding some marker for inherited disease which could lead to their early treatment. In 1985 Jeffrey founded DNA of each individual has some non-cistronic hyper -variable repeat mini satellite f
sequences. This repeat many satellite sequence flanked by conserve restriction site are now commonly called VNTRs or variable number of tandem repeats. DNA fingerprinting is highly reliable method of identification of individuals involve in rape murder and other crimes.
MCQ ON THE DNA FINGERPRINTING class 12 for NEET
1.The DNA fingerprinting involves identifying differences in some specific regions in DNA sequence called as
(a) non repetitive DNA
(b) repititive DNA
(c) Exons
(d) all the above
Ans (b) repetitive DNA
2. The repetitive DNA are separated from bulk genomic DNA as different peaks during density gradient ……..
(a) centrifugation
(b) mRNA
(c) Repressor protein
(d) centripetal
Ans. (a) centrifugation
3. The bulk DNA forms a major peak and the other small peaks are referred to as
(a) satellite DNA
(b) X DNA
(c) Y DNA
(d) Z DNA
Ans. (a) satelite DNA
4. Basis of DNA fingerprinting is
(a) satellite DNA
(b) high degree of polymorphism
(c) beta galactosidase
(d) endonuclease
Ans.(b) high degree of polymorphism
5.Basis of paternity test in case of disputes
(a) DNA fingerprinting
(b) DNA replication
(c) DNA translation
(d) DNA transcription
Ans.(a) DNA fingerprinting
6. Basis of genetic map of human genome as well as DNA fingerprinting is
(a) repetitive DNA
(b) satellite DNA
(c) DNA polymorphism
(d) SNP
Ans.(c) DNA polymorphism
7. Polymorphism variation at genetic level arises due to
(a) mutation
(b) crossing over
(c) gene expression
(d) natural selection
Ans.(a) mutation
8. The technique of Fingerprinting was initially developed by
(a) Alec Jeffreys
(b) Mendel
(c) Morgan
(d) none of the above
Ans.(a) Alec Jeffreys
9. Alex Jeffrey used a which DNA as a probe that show very high degree of polymorphism.
(a) repressor
(b) satellite DNA
(c) repetitive DNA
(d) all the above
Ans. (b) satellite DNA
10. VNTR is related to
(a) amniocentesis
(b) DNA replication
(c) DNA fingerprinting
(d) none of the above
Ans. (c) DNA fingerprinting
11. The VNTR belongs to a class of Satellite DNA referred to as
(a) mini – satellite
(b) beta galactose
(c) micro-satellite
(d) all the above
Ans.(a) mini- satellite
12. DNA fingerprinting analysis used in
(a) application in forensic science
(b) determining population
(c) genetic diversity
(d) all the above
Ans . (d) all the above
13.In DNA fingerprinting analysis is made of
(a) Satellite DNA
(b) moderately repetitive sequences
(c) micro satellites
(d) variable number of tandem repeats
Ans.(d) variables number of tendem repeats
15. Matching DNA sequence of criminal with suspect is known as
(a) DNA mapping
(b) DNA fingerprinting
(c) DNA resolution
(d) all the above
Ans. (b) DNA fingerprint
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
16. Which cannot be used for DNA fingerprint in humans?
(a) leucocytes
(b) Erythrocytes
(c) hair bulbs
(d) sperms
Ans.(b) Erythrocytes
17. Basis of DNA fingerprinting is
(a) double helix
(b) error in base sequence
(c) polymorphism in sequence
(d) DNA replication
Ans.(c) polymorphism in sequence
18. Which is not in application of DNA fingerprinting
(a) solving immigration cases
(b) solving paternity cases
(c) curing SCID
(d) identifying gene mutation
And.(c) curing SCID
19. The probs for DNA fingerprintings are
(a) Anand single standard lebelled DNA
(b) unknown double standard lebelled DNA
(c) known single standard lebelled DNA
(d) Known double standard unlabelled DNA
Ans. (c) Known single standard lebelled DNA
20. VNTRs are
(a) variable number of tandem repeats
(b) very narrow tendem repeats
(c) variable nonstronic transponse repeats
(d) all the above
Ans.(a) variable number of tandem repeats







Leave a Comment