MCQ ON ROOT AND REGIONS OF ROOT / ROOT AND REGIONS OF ROOT class 11 for NEET | ROOT AND REGIONS OF ROOT class 11| MCQ ROOT AND REGIONS OF ROOT with Answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 11Biology based on the with Answers.
MCQ on ROOT AND REGIONS OF ROOT 11Biology with answers were prepared based on the latest pattern.We have provided class 11 Biology MCQs question with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
MCQ ON ROOT AND REGIONS OF ROOT / ROOT AND REGIONS OF ROOT class 11 for NEET
MCQ ON ROOT AND REGIONS OF ROOT is useful for NEET / CSIR / UGC / CBSE / ICSE / AIIMS / EXAM / AFMC EXAM / STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM/ KVS PGT BIOLOGY / NVS PGT BIOLOGY EXAM 2023-2024 ,2025
INTRODUCTION:-
ROOT AND REGIONS OF ROOT:-
In majority of dicotyledonous plants the direct elongation of the radicle leads to the formation of primary root which grows inside the soil.
It bears lateral roots of several orders that are referred to as secondary, tertiary, etc roots.
The primary root and it’s branches constitute the tap root system as seen in mustard plant.
In monocotyledonous plants the primary root is short lived and is replaced by a large number of roots .
These roots originate from the base of the stem and constitute the fibrous root system as seen in wheat plant.
In some plants like grass , monstera and the banyan tree , root arise from parts of the plants other than the radicle and are called adventitious roots
The main function of the root system are absorption of water and minerals from the soil and providing a proper anchorage to the plants parts.
It stores food material and synthesis of plant growth regulators.
REGIONS OF THE ROOT:-
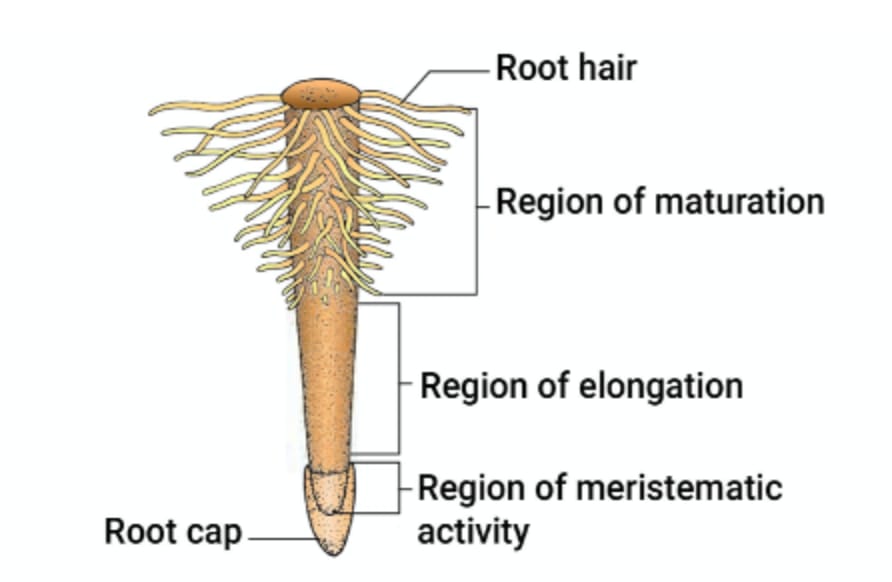
The root is covered at the apex by a thimble like structure called the root cap.
It protects the tender apex of the root as it makes its way through the soil.
A few millimetres above the root cap is the region of merismetic activity.
The cells of merismetic activity are very small thin walled and with dense protoplasm.
They divide repeatedly. The cells proximal to this region undergo rapid elongation and enlargement and responsible for the growth of the root in length.
This region is called region of elongation.
The cells of elongation zone gradually differentiated and mature . Hence this zone proximal to region of elongation is called the region of maturation.
Region of maturation , a thread like structure root hairs originated.
These roots hairs absorb water and minerals from the soil.
MODIFIED STEM
:-The stem may not always be typically like what they are expected to be.
They are modified to perform different functions.
Underground stems of potato , ginger , turmeric , zamikand , colocasia are modified to store food in them.
They also act as an organs of perennetation to tide over conditions unfavourable for growth.
Stems tendris which develop from axillary buds , are slender and spirally coiled and helps plants to climb such as in gourds ( cucumber , pumpkins , watermelon ) and grapevines .
Axillary buds of stems may also get modified in many plants such as citrus , Bougainvillea .
They protect plant from browsing animals.Some plants of arid regions modified their stems into flattened (opuntia) or fleshy cylindrical ( euphorbia) structures.
They contain chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis.
Underground stems of some plants such as grass and strawberry etc spread to new niches and when older parts die new plants are formed.
PHYLLOTAXY:-
phyllotaxy is the pattern of arrangement of leaves on the stem or branch. This is usually of three types – alternate phyllotaxy , opposite phyllotaxy and whorled phyllotaxy.
Alternate phyllotaxy:- In alternate phyllotaxy type of phyllotaxy a single leaf arises at each node in alternate manner as in China rose, Mustard and sunflower plants.
Opposite phyllotaxy:- In opposite phyllotaxy a pair of leaves arise at the each node and lie opposite to each other as in calotropis and guava plants.
Whorled phyllotaxy:-
If more than two leaves arise at each node and a form a whole , it is called whorled as in Alstonia
CALYX:-
Calyx is the outermost whorl of the flower and the members are called sepals.
Generally , sepals are green , leaf – like and protect the flower in the bud stage.The calyx may be gamopetalous sepals united or polysepalous sepals free.
COROLLA:-
Corolla is composed of petals.Petals are usually brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination. Like calyx corolla may be also united gamosepalous petals united or polysepalous petals free.
The shape and colour of Corolla vary greatly in plants.
Corolla may be tubular , bell-shaped , funnel – shaped or wheel – shaped.
GYNOECIUM :-
Gynosium is the female reproductive part of the flower and is made of one more carpels.
A carpel consist of three parts namely stigma style and ovary.
Ovary is the enlarged basal part , on which lies the elongated tube, the style .
The style connects the ovary to the stigma.
Stigma is the usually tip of the style and is the receptive surface for pollen grains .
Each ovary bears one or more ovules attached to a flattened, cushion like placenta.
When more than one carpel is present , there may be free as in Lotus and rose and are called Apocarpous.
They are termed as Syncarpous when carpels are fused as in mustard and tomato.
After fertilisation , the ovules develop into seeds and the ovary matures into a fruit.
Androecium is composed of stamens.Each stamens which represents the male reproductive organ consists of a stalk or a filament and an anther.
Each anther is usually bilobed and each lobe has two chambers , the pollen sacs. The pollen grains are produced in pollen-sacs.A sterile stamen is staminode .
Stamens of flower may be united with other members such as petals or among themselves .
When stamens are attached to the petals , they are epipetalous as in brinjal
Epiphyllous when attached to the perianth as in the flower of Lily.
The stamens in a flower may either remain free ( polyandrous) or may be united in varying degrees .
The stamens may be united into bunch or one bundle ( monoadelphous) as in China rose or two bundles (diadelphous) as in pea , or into more than two bundles (polydelphous) as in citrus.
There may be variations in the length of filaments within a flower as in salvia and mustard.
MCQ ON ROOT AND REGIONS OF ROOT class 11 for NEET/KVS PGT BIOLOGY / NVS PGT BIOLOGY EXAM 2023-2024,2025
1. Ine majority of the dicotyledonous plants the direct elongation of the radicle leads to the formation of
(a) primary root
(b) axillary buds
(c) apical buds
(d) all the above
Ans (a) primary root
2. The primary roots and a branches constitute the
(a) fibrous root system
(b) tap root system
(c) phyllotaxy
(d) none of the above
Ans. (b) tap root system
3. mustard plant contains
(a) fibrous root
(b) adventitious root
(c) tap root
(d) thorns
Ans. (c) tap root
4.In wheat plant contains
(a) tap root
(b) fibrous root
(c) both a and b
(d) colocasia
Ans.(b) fibrous root
5. The root arise from parts of the plant other than the radicle and are called
(a) tap root system
(b) fibrous root
(c) adventitious root
(d) all the above
Ans.(c) adventitious root
6. In grass, monstera and banyan tree contain
(a) tap root
(b) fibrous root
(c) adventitious root
(d) all the above
Ans.(c) adventitious root
7. The main function of the root system are
(a) absorption of water
(b) proper anchorage to plant parts
(c) plant growth regulators
(d) all the above
Ans.(d) all the above
8. The root is covered at the apex by a thimble – like structure called the
(a) elongation
(b) maturation region
(c) root cap
(d) radicle
Ans.(c) root cap
9. A few millimetres above the root cap is the
(a) region of elongation
(b) region of maturation
(c) region of merismetic activity
(d) all the above
Ans. (c) region of merismetic activity
10. Which are the characteristics of region of mathematic activity
(a) very small thin walled
(b) with dense protoplasm
(c) divide repeatedly
(d) all the above
Ans. (d) all the above
11. The cells responsible for growth of the root in length
(a) region of merismetic
(b) region of maturation
(c) region of elongation
(d) all the above
Ans.(c) region of elongation
12. The zone proximal to region of elongation is
a) merismetic activity
b) region of maturation
c) region of elongation
(d) all the above
Ans . (b) region of maturation
13. Root hairs originated from
(a) region of elongation
(b) region of maturation
(c) region of merismetic
(d) all the above
Ans.(d) region of maturation
14. The function of root hairs
(a) absorb water and minerals from the soil
(b) assimilation of food
(c) translocate
(d) all the above
Ans. (a) absorb water and minerals from the soil
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
15. From the region of maturation some of the epidermal cells form very fine and delicate thread – like structures called
(a) root hairs
(b) arid region
(c) temperate regions
(d) root cap
Ans.(a) root hairs
16. Which is not adventitious root
(a) monstera
(b) grass
(c) Banyan tree
(d) wheat
Ans.(d) wheat







Leave a Comment