MCQ ON MUTATIONS class 12 for NEET | MUTATIONS class 12 | MCQ MUTATIONS with Answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 12 Biology based on the with Answers.
MCQ ON MUTATIONS class 12 for NEET
MCQ on MUTATIONS class 12 Biology with answers were prepared based on the latest pattern.We have provided class 12 Biology MCQs questions on MUTATIONS with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
MCQ ON MUTATIONS is useful for NEET / CSIR / UGC / CBSE / ICSE / AIIMS / EXAM / AFMC EXAM / STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM 2022-23, 2023-24
Introduction:
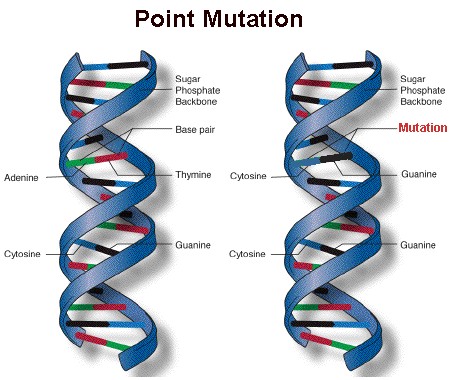
Mutation is a phenomenon which results in alternation of DNA sequences and consequently results in changes in the genotype and the phenotype of an organism.In addition to recombination, mutation is another phenomenon that leads to variations in DNA.
There are many chemical and physical factors that induce Mutations.These are referred to as mutagens.UV radiation can cause mutations in organism – it is a mutagen.
MCQ ON MUTATIONS class 12 for NEET
1. The term mutation was coined by
(a) Hugo de Vries
(b) Bateson
(c) Lamarck
(d) Morgan
Ans (a) Hugo de Vries
2. Who proposed mutations theory of evolution
(a) Hugo de Vries
(b) lamarck
(c) Darwin
(d) Mendel
Ans. (a) Hugo de Vries
3. Huge de Vries observed mutations on plants
(a) pea
(b) oenothera lamarckiana
(c) chrysanthemum
(d) all the above
Ans. (b) oenothera lamarckiana
4. The condition in which chromosome number exact multiple of genome
(a) aneuploidy
(b) euploidy
(c) polyploidy
(d) all the above
Ans.(b) euploidy
5. Polyploids with odd number of genome are sexually …..
(a) fertile
(b) sterile
(c) induced
(d) aberration
Ans.(b) sterile
6. Alkaloid a mitotic poisonous which inhibits spindle formation without affecting replication of chromosomes.
(a) caffeine
(b) opium
(c) colchicine
(d) arginine
Ans.(c) colchicine
7. The gene mutation involves a change in single nucleotide pair.
(a) frameshift mutations
(b) point mutations
(c) deletion
(d) assertion
Ans.(b) point mutations
8. A mutations from wild to a new type is called
(a) forward mutation
(b) back mutations
(c) point mutations
(d) none of the above
Ans.(a) forward mutation
9. The reversal of mutated gene back to its original form is called
(a) reverse mutations
(b) point mutations
(c) frameshift mutations
(d) all the above
Ans. (a) reverse mutations
10. Mutations affecting vegetative cells are
(a) somatic mutations
(b) germinal mutations
(c) dominant mutations
(d) none of the above
Ans. (a) somatic mutations
11. The mutations which occurs in sex cells and are inheritable
(a) point mutations
(b) germinal mutations
(c) somatic mutations
(d) all the above
Ans.(b) germinal mutations
12. A single mutations affecting more than one characters is called
(a) pleiotropic mutations
(b) dominant mutations
(c) recessive mutations
(d) none of the above
Ans . (a) pleiotropic mutations
13. The physical and chemical factors which brings about new mutations
(a) allele
(b) mutagens
(c) radiation
(d) lethargic
Ans.(b) mutagens
15. Which can induce polyploidy?
(a) colchicine
(b) acridine
(c) ethylene
(d) all the above
Ans. (a) colchicine
16. Mutations can be brought by
(a) aniline dye
(b) X- rays
(c) auxins
(d) DDT
Ans.(b) X-rays
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
17.Colchocine intefers with
(a) chromosome replication
(b) organisation of spindle
(c) chromosome condensation
(d) incorporation of nitrogen bases
Ans.(b) organisation of spindles
18. The major / ultimate source of variations are
(a) polyploidy
(b) mutations
(c) chromosome aberration
(d) segregation
And.(b) mutations
19. Recessive mutations are expressed in
(a) homozygous condition
(b) heterozygous condition
(c) next generation
(d) same generation
Ans. (a) homozygous condition
20.Muller was awarded Nobel prize in 1946 for his work in
(a) proteins synthesis
(b) cancer
(c) AIDS
(d) X- ray induced mutations
Ans.(d) X- rays mutations
21. Mutations are commonly
(a) dominant
(b) codominant
(c) recessive
(d) incomplete
Ans. (c) recessive
22. The gene that controls the rate of mutations of another gene is
(a) regulator gene
(b) inducer gene
(c) mutable gene
(d) mutators gene
Ans.(d) mutators gene







Leave a Comment