MCQ ON GENETIC DRIFT class 12 for NEET | GENETIC DRIFT class 12 | MCQ GENETIC DRIFT with Answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 12 Biology based on the with Answers.
MCQ ON GENETIC DRIFT class 12 for NEET
MCQ on GENETIC DRIFT class 12 Biology with answers were prepared based on the latest pattern.We have provided class 12 Biology MCQs questions on GENETIC DRIFT with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
MCQ ON GENETIC DRIFT is useful for NEET / CSIR / UGC / CBSE / ICSE / AIIMS / EXAM / AFMC EXAM / STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM 2022-23, 2023-24
Introduction:
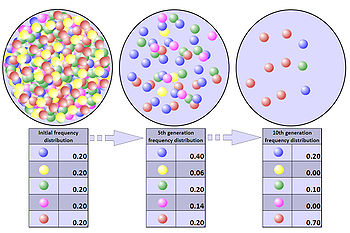
Evolutionary biology is the study of history of life forms on earth.To understand the changes in flora and fauna that have occurred over millions of years on earth , we must have an understanding of the context of origin of life , of stars, of earth and indeed universe itself.This is the story of origin of life and evolution of life forms or biodiversity on planet earth in the context of evolution of earth and against the background of evolution of Universe itself. Evolution is revealing of hidden potential ties that bring about an orderly change from one condition to another.Cosmic evolution deals with the sequence of changes that occur in inorganic matter and its evolution. Darwinism or theory of natural selection is a theory of organic evolution which states that newly species evolve over a long period of time through accumulation of small variation which provides organisms overs structural and functional superiority over others In their survival and differential reproduction. A species may have several populations in a random change in allele number and frequency in a gene pool due to chance. Genetic drift variabilities also limited it leads to fixation of certain alleles and elimination of others. Chance factor mein increase the frequency of a trait which may or may not have any adaptive value.
MCQ ON GENETIC DRIFT class 12 for NEET
1. The random change in allele number and frequency in a gene pool due to chance is called
(a) natural selection
(b) mutation
(c) genetic drift
(d) saltation
Ans (c) genetic drift
2. Genetic drift occurs in
(a) large size of population
(b) small size of population
(c) both a and b
(d) discontinuous variation
Ans. (b) small size of population
3. Genetic drift is caused by
(a) sampling error
(b) genetic bottle neck effect
(c) sewall wright effect
(d) all the above
Ans. (d) all the above
4. The effect of genetic drift are
(a) increase in inbreeding
(b) decrease in heterogosity
(c) increase in homozygosity
(d) all the above
Ans.(d) all the above
5. Due to genetic drift a different genepool and a different population change in phenotypic forms forms a new species such mechanism of speciation is called
(a) founder effect
(b) allele effect
(c) genetic effect
(d) Wallace effect
Ans.(a) founder effect
6. Reduction in allele frequencies during the brief reduction in size of population is called
(a) founder effect
(b) genetic bottle neck effect
(c) Wright effect
(d) both b and c
Ans.(d) both b and c
7. Genetic drift
(a) is random change in gene frequency
(b) has nothing in common with in breeding
(c) is an orderly change in gene frequency
(d) produces greatest fluctuation in large population
Ans.(a) is random change in gene frequency
8. Genetic drift is found in
(a) small population or without mutated gene
(b) large population with random mating
(c) animal population
(d) plant population
Ans.(a) small population with or without mutated gene
9. Random genetic drift in a population probably results from
(a) highly genetically variable individuals
(b) inter breeding between small population
(c) constant Low motation rate
(d) large population size
Ans. (b) inter breeding within small population
10. In random mating population in equilibrium which of the following brings about change in gene frequency in non directional manner
(a) mutation
(b) random drift
(c) selection
(d) migration
Ans. (b) random drift
11. Concept of genetic drift was introduced by
(a) Sewal Wright
(b) Hardy Weinberg
(c) Julian Huxley
(d) Simpson
Ans.(a) Sewal Wright
12. Chance elimination of allele from a small population is an example of
(a) adaptation
(b) genetic drift
(c) speciation
(d) mutations
Ans . (b) genetic drift
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
13. Maintenance of genetic equilibrium is known as
(a) gause principle
(b) burgman law
(c) glogger principle
(d) Hardy Weinberg principle
Ans.(d) Hardy Weinberg principle
15. A brief reduction in size of population due to natural calamities leads to random genetic drift. For this statement identify the correct example
(a) long neck giraffe
(b) industrial melanism
(c) human population of Pitcairn Islands
(d) polydactylic dwarfs in amish population
Ans. (d) polydactylic dwarfs in amish population
16. Variation in gene frequency within population can occur by chance rather than by natural selection. This is referred to as
(a) genetic load
(b) genetic flow
(c) genetic drift
(d) random mating
Ans.(c) genetic drift
17. Random unidirectional change in allele frequencies that occurs by chance in all populations and specially in a small population is known as
(a) natural selection
(b) sexual reproduction
(c) genetic drift
(d) mutation
Ans.(c) genetic drift
18. Which one is sewall wright effect
(a) isolation
(b) gean pool
(c) genetic drift
(d) polyploidy
Ans.(c) genetic drift
19. Which mechanism of evolution affects genetic makeup of a population
(a) isolation and mutation
(b) genetic drift
(c) isolation and competition
(d) isolation and variation
Ans. (b) genetic drift
20. Occurrence of non beneficial alleles in heterozygous genotype is
(a) genetic load
(b) genetic drift
(c) gene flow
(d) intra specific breeding
Ans.(a) genetic load
21. Gene frequency in a population remains stable unless and until there is
(a) random drift
(b) random mating
(c) selection
(d) mutation
Ans.(c) selection







Leave a Comment