MCQ ON EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION class 11 for NEET | EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION class 11 | MCQ EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION with Answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 11 Biology chapter 19 based on the EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION with Answers.
MCQ ON EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION class 11
MCQ on EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION class 11 Biology with answers were prepared based on the latest pattern.We have provided class 11 Biology MCQs questions on EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
MCQ EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION is useful for NEET / CSIR / UGC / CBSE / ICSE / AIIMS / EXAM / AFMC EXAM / STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM 2022-23, 2023-24
Introduction:-
Animals accumulate ammonia , urea , uric acid , carbon dioxide , water and ions like Na+, K+ , Cl- , phosphate , sulphate , etc , either by metabolic activities or by other means like excess ingestion.These substances have to be removed totally or partially.Ammonia , urea and uric acid are the major forms of nitrogenous waste excreted by the animals.
MCQ ON EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION class 11 for NEET
1.The most toxic excretory products
(a) ammonia
(b) urea
(c) uric acid
(d) all the above
Ans (a) ammonia
2. The least toxic products
(a) ammonia
(b) uric acid
(c) urea
(d) none of the above
Ans. (b) uric acid
3. Many bony fishes, aquatic amphibians and aquatic insects are
(a) ureotelic
(b) ammonotelic
(c) uricotelic
(d) none of the above
Ans. (b) ammonotelic
4. Mammals, many terrestrial amphibians and marine fishes are
(a) ammonotelic
(b) uricotelic
(c) ureotelic
(d) none
Ans.(c) ureotelic
5. Reptiles, birds , land snails and insects are
(a) ureotelic
(b) uricotelic
(c) ammonotelic
(d) none
Ans.(b) uricotelic
6. The excretory organ of planaria
(a) flame cells
(b) green glands
(c) malpighian tubules
(d) nephridia
Ans.(a) flame cells
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
7. The excretory organ of annelids
(a) malpighian tubules
(b) green glands
(c) antennal glands
(d) nephridia
Ans.(d) nephridia
8. The excretory function of cockroach
(a) green glands
(b) malpighian tubules
(c) nephridia
(d) kidney
Ans.(b) malpighian tubules
9. The excretory function in prawn
(a) green glands
(b) malpighian tubules
(c) flame cells
(d) protonephridia
Ans. (a) green glands
10. Column of Bertini belong to
(a) lungs
(b) kidney
(c) liver
(d) heart
Ans. (b) kidney
11. The functional units of kidney
(a) neuron
(b) nephron
(c) alveoli
(d) none
Ans.(b) nephron
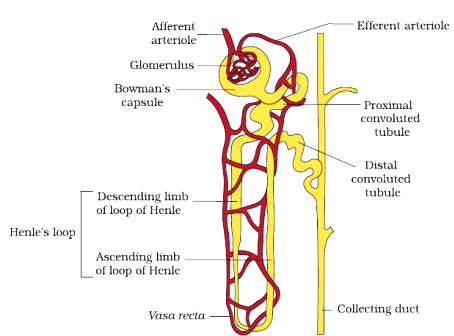
12. Malpighian body or renal corpuscles encloses
(a) glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule
(b) glomerulus and PCT
(c) glomerulus and DCT
(d) none of the above
Ans.(a) glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule
13. The malpighian tubules , PCT and DCT of the nephron are situated in the …..
region of the kidney
(a) cortical
(b) medulla
(c) both a and b
(d) none of the above
Ans. (a) cortical
14. The Loop of Henle dips into the
(a) cortical
(b) medulla
(c) glomerulus
(d) Bowman’s capsule
Ans.(b) medulla
15. A minute vessel of the network runs parallel to the Henle’s Loop forming a U shaped
(a) podocyte
(b) vasa recta
(c) column of Bertini
(d) ultra filtration
Ans. (b) vasa recta
16.Urine formation involves
(a) glomerular filtration
(b) reabsorption
(c) secretion
(d) all the above
Ans.(d) all the above
17. The epithelial cells of Bowman’s capsule
(a) podocyte
(b) vasa recta
(c) ultra filtration
(d) glomerular filtration
Ans.(a) podocyte
18. Glomerular filtration rate in a healthy individual is
(a) 180 litres per day
(b) 200 litres per day
(c) 220 litres per day
(d) all the above
And.(a) 180 litres per day
19. An increase in blood flow to the atria of the heart can cause release of ………which decrease the blood pressure.
(a) Renin
(b) angiotensin
(c) Atrial Natriuretic Factor.
(d) ADH
Ans. (c) Atrial Natriuretic Factor
20. The process of release of urine
(a) micturition
(b) parturition
(c) glycosuria
(d) none of the above
Ans.(a) micturition
21.Presence of glucose and ketone bodies in urine are indicative of
(a) diabetes insipidius
(b) diabetes mellitus
(c) renal calculi
(d) renal failures
Ans. (b) diabetes mellitus







Leave a Comment