MCQ ON TRANSLATION class 12 for NEET | TRANSLATION class 12 | MCQ TRANSLATION with Answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 12 Biology based on the with Answers.
MCQ on TRANSLATION class 12 Biology with answers were prepared based on the latest pattern. We have provided class 12 Biology MCQs question with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
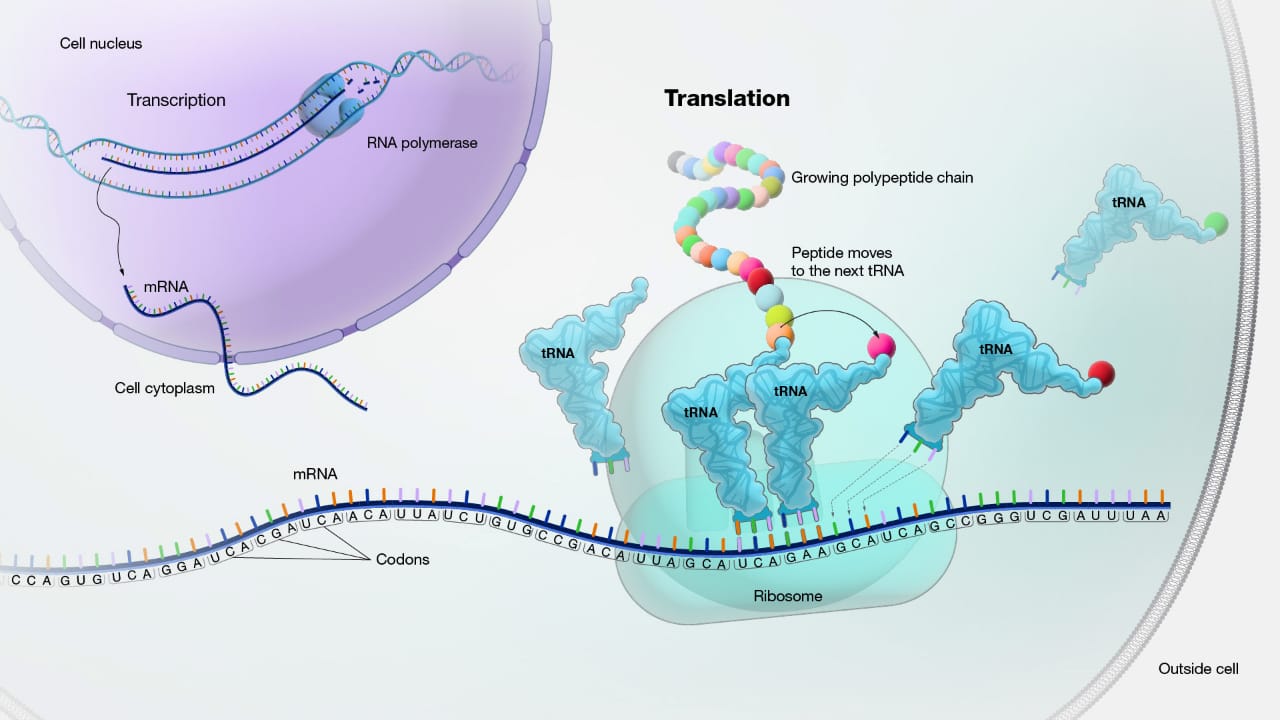
MCQ ON TRANSLATION class 12 for NEET
MCQ ON TRANSLATION is useful for NEET / CSIR / UGC / CBSE / ICSE / AIIMS / EXAM / AFMC EXAM / STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM/ KVS PGT BIOLOGY / NVS PGT BIOLOGY EXAM 2023-2024 ,2025
INTRODUCTION:-
TRANSLATION:-
Translation refers to the process of polymerization of amino acids to form a polypeptide. The order is sequence of amino acids are defined by the sequence of bases in the mRNA. Amino acids are joined by a bond which is known as peptide bond.
Formation of peptide bond required energy.
Therefore in the first phase itself amino acid are activated in the presence of ATP cognate tRNA – a process commonly called as charging of tRNA or aminoacylation of tRNA to be more specific.
If two such charged tRNAs are brought close enough the formation of peptide bond between them would be favoured energetically. The presence of a catalyst would enhance the rate of peptide bond formation.
The cellular factory responsible for synthesizing proteins is the ribosome.
Gregor Johann Mendel is known as father of genetics. The term genetics was coined by Bateson.
Genetics is the study of principal and mechanism of heredity and variations.
Genetics has three branches :
-transmission genetics :- classical mandelian genetics studies transmission of genesfrom generation to generation.
Molecular genetics:- study genes and their working at the molecular level.
Population genetics:- studies distribution spread and changes in gene in population.
Variations:- variations are differences found in morphological physiological cytological and behaviour traits of individuals belonging to same species, race and family.
Variation occurs due to
Crossing over, chance combination of chromosomes during meiosis and fertilization.
Johannsen defined gene to be elementary unit of inheritance that specifies the expression of a particular traits .
Characteristics of genes :-
Gene store and express coded information of hereditary nature.
Genes can undergo replication so that copies can be transmitted to daughter cells as well as offspring.
They can occasionally undergo mutation.
Genes are located over chromosome.
All the genes donot express simultaneously.
There is a system of differential expression.
It results in development and differentiation.
MCQ TRANSLATION class 12 for NEET/KVS PGT BIOLOGY / NVS PGT BIOLOGY EXAM 2023-2024,2025
1. Protein synthesis occurs over
(a) ribosomes
(b) mitochondria
(c) Golgi apparatus
(d) lysosome
Ans (a) ribosomes
2.The ribosomes of a polyribosomes are held together by
(a) tRNA
(b) mRNA
(c) ribosomes RNA
(d) all the above
Ans. (b) mRNA
3. The process of attachment of tRNA with its specific amino acid is called
(a) charging
(b) Transposon
(c) initiation factors
(d) Recon
Ans. (c) initiation factors
4. The process of polymerization of amino acid to form a polypeptide is called
(a) Translation
(b) transcription
(c) gene regulation
(d) Constitutive enzyme
Ans.(a) translation
5. The orders of amino acids are defined by the sequence of bases in the
(a) tRNA
(b) mRNA
(c) rRNA
(d) all the above
Ans.(b) mRNA
6. Amino acids are joined by a bond which is known as
(a) Glycosidic bonds
(b) 5′ capping
(c) Polyadenylation
(d) peptide bond
Ans.(d) peptide bond
7. The first phase of translation process is
(a) charging of tRNA
(b) untranslated region
(c) release factor
(d) Anti codon
Ans.(a) charging of tRNA
8. The cellular factory responsible for synthesizing protein
(a) mitochondria
(b) polysaccharide
(c) ribosomes
(d) chloroplast
Ans.(c) ribosomes
9. The ribosome consists of
(a) structural RNA and 80 different proteins
(b) structural DNA and 70 different proteins
(c) Glycosidic bonds
(d) Phosphodiester bonds
Ans. (a) structural RNA and 80 different proteins
10. The ribosome acts as a catalyst for the formation of peptide bond .
(a) ribozymes
(b) hydrolase
(c) constitute
(d) initiation codon
Ans. (a) ribozymes
11. Translational unit in mRNA is a sequence of RNA that is flanked by the start codon.
(a) AUG
(b) UAA
(c) UAG
(d) UGA
Ans.(a) AUG
12. In master RNA has some additional sequences that are not translated in and referred as
a) untranslated region (UTR).
b) stop codon
c) release factor
(d) Transformation
Ans . (a) untranslated region (UTR)
13.The UTRs are present at
(a) 5′ end
(b) 3 ‘ end
(c) both 5′ end and 3′ end
(d) Operon
Ans.(c) both 5′ end and 3’ end
14.For initiation the ribosome binds to the mRNA at the start codon AUG that is recognised only by the
(a) initiator t RNA
(b) release factor
(c) charging m RNA
(d) UGG
Ans. (a) initiator tRNA
15.Amino acids are added one by one translated into polypeptide sequence dictated by DNA and represented by
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) Adenosine deaminases
(c) mRNA
(d) Topoisomerase
Ans.(c) mRNA
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
16. At the end which factors binds to the stop codon , terminate translation and release the complete polypeptide from ribosomes.
(a) DNA Topoisomerase
(b) release factor
(c) DNA polymerase
(d) Reverse transcriptase
Ans.(b) release factor







Leave a Comment