MCQ ON REGULATIONS OF KIDNEY FUNCTION class 11 for NEET | REGULATION OF FUNCTION class 11 | MCQ REGULATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTION with Answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 11 Biology based on the with Answers.
MCQ on REGULATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTION class 11 Biology with answers were prepared based on the latest pattern. We have provided class 11 Biology MCQs question with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
MCQ ON REGULATIONS OF KIDNEY FUNCTION is useful for NEET / CSIR / UGC / CBSE / ICSE / AIIMS / EXAM / AFMC EXAM / STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM/ KVS PGT BIOLOGY / NVS PGT BIOLOGY EXAM 2023-2024 ,2025
MCQ ON REGULATIONS OF KIDNEY FUNCTION class 11 for NEET
INTRODUCTION:-
REGULATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTION :-
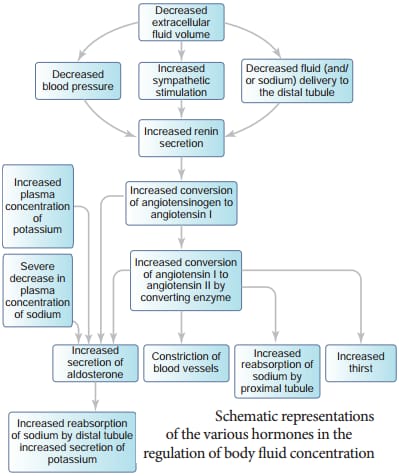
THE FUNCTIONING OF THE KIDNEY IS efficiently monitored and regulated by hormonal feedback mechanism involving the hypothalamus,JGA and to a certain extent the heart.
PROXIMAL COONVULATED TUBULE is lined by simple cuboidal brush border epithelium which increases the surface for reabsorption. Nearly old essential nutrients and 70 to 80% of electrolytes in water are reabsorbed by this segment.
Pct also helps to maintain the pH and ionic balance of the body fluid by selective secretion of hydrogen ions ammonia and potassium ions into the field trade and by the absorption of bicarbonate from it.
Loop of Henle :- reabsorption in this segment is minimum.
This region plays a significant role in the maintenance of high osmolarity of medullary interstitial fluid.
The descending limb of loop of Henle is permeable to water and almost impermeable to electrolytes.
This concentrates the filtrate as it moves down.
The ascending limb is impermeable to water but allows transport of electrolytes actively or passively.
DISTAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE:-
It helps in the conditional reabsorption of sodium ions and and water takes place in the segment. The DCT is also capable of reabsorption of bicarbonate ions and selective secretion of hydrogen and potassium ions.
Collecting duct:- this long dog extends from the cortex of the kidney to the inner parts of the medulla. Large amounts of water could be reabsorbed from this region to produce a concentrated urine. This sigment allows passage of small amounts of India into the medullary interstitium to keep up the osmolarity.
Urine formation involves three main processes namely glomerular filtration, reabservation and secretion, that takes place in different parts of the nephron.
The first step in urine formation is the filtration of blood, which is carried out by the Glomerular and is called glomerulus filtration.
On in average 1100 to 1200 ml of blood is filtered by the kidney per minute which constitution roughly 1/ 5 of the blood pump out by each ventricle of the heart in a minute. The glomerular capillary blood pressure causes filtration of blood through three layers the endothelium of glomerular blood vessels, the epithelial of bowman’s capsule and basement membrane between these two layers.
Bloody is filtered so finally through the basement membrane that allow almost all the constituent of the plasma except the protein pass on to the lumen of the bowman’s capsules. Therefore it is considered as a process of ultra filtration.
The amount of filtrate formed by the kidney per minute is called Glomerular filtration rate.
GFR in healthy individual is approximately 125 ml per minute that is 180 liters per day.
The kidney have built in mechanism for a regulation of glomerular filtration rate.
One such efficient mechanism is carried out by justa glomerular apparatus.
JGA is a special sensitive region formed by cellular modification in the DCT.
MCQ REGULATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTION class 11 for NEET/KVS PGT BIOLOGY / NVS PGT BIOLOGY EXAM 2023-2024,2025
1. Mammals have the ability to produce a concentrated urine . The segment which player significant role in this
(a) PCT
(b) Henle’s loop
(c) vasa recta
(d) both b and c
Ans (d) both b and c
2. The flow of filtrate in the two limbs of Henle loop is in opposite directions and thus forms a
(a) maintain the pH
(b) maintain ionic balance of the body fluid
(c) selective secretion of hydrogen ions
(d) counter current
Ans. (d) counter current
3. The flow of blood through the two limbs of vasa recta is in the patterns of
(a) counter current
(b) DCT
(c) GFR
(d) CD
Ans. (a) counter current
4. Which help in maintaining increasing osmolarity towards the inner medullary interstitium from 300 mOsmol per litre in the cortex to about 1200 mOsmol per litre in the inner medulla.
(a) loop of Henle
(b) vasa recta
(c) counter current
(d) all the above
Ans.(d) all the above
5. Transport of substances facilitated by the special arrangement of henle’s loop and vasa recta is called the
(a) PCT
(b) DCT
(c) Henle’ sloop
(d) counter current mechanism
Ans.(d) counter current mechanism
6. The functioning of the kidney is efficiently monitored and regulated by hormonal feedback mechanism involving the
(a) hypothalamus
(b) JGA
(c) The heart
(d) all the above
Ans.(d) all the above
7. Osmoreceptors in the body are activated by change in
(a) blood volume
(b) body fluid volume
(c) and ionic concentration
(d) all the above
Ans.(d) all the above
8. An excess loss of fluid from the body can activate receptors which stimulate the hypothalamus to release hormone
(a) PCT
(b) ADH
(c) loop of Henle
(d) collecting duct
Ans.(b) ADH
9. ADH facilitates water reabsorption from latter parts of the tubule threby preventing
(a) PCT
(b) diuresis
(c) JGA
(d) UFR
Ans. (b) diuresis
10. ADH or vasopressin is released by
(a) PCT
(b) adenohypophysis
(c) neurohypophysis
(d) Bowman’s capsule
Ans. (c) neurohypophysis
11. Which plays a complex regulatory role ?
(a) Collecting duct
(b) PCT
(c) JGA
(d) rennin
Ans.(c) JGA
12.A fall in glomerular blood flow can activate the JG cells to release …….hormone which converts angiotensinogen in blood to angiotensin I and further to angiotensin II .
a) renin
b) vasopressin
c) hypothalamus
(d) collecting duct
Ans . (a) renin
13. Which is being a powerful vasoconstrictor
(a) Angiotensinogen II
(b) secretion
(c) reabsorption
(d) collecting duct
Ans.(a) Angiotensinogen II
14. Which hormone causes reabsorption of sodium ions and water from the distal parts of the tubule.
(a) aldosterone
(b) a pairs of ureters
(c) urinary bladder, urethra
(d) ADH
Ans. (a) aldosterone
15. An increase in blood flow to the artria of the heart can cause the release of
(a) Atrial Natriuretic Factor
(b) oval shape
(c) bean shaped structure
(d) cylindrical
Ans.(a) Atrial Natriuretic Factor
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
16. ANF can cause of vasodilation and thereby decrease by the
(a) renal pelvis
(b) blood pressure
(c) tubular secretion
(d) passive transport
Ans.(b) blood pressure







Leave a Comment