MCQ ON EPIDERMAL TISSUE SYSTEM / EPIDERMAL TISSUE SYSTEM class 11 for NEET | EPIDERMAL TISSUE SYSTEY class 11| MCQ ON EPIDERMAL TISSUE SYSTEM with Answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 11Biology based on the with Answers.
MCQ on EPIDERMAL TISSUE SYSTEM class 11Biology with answers were prepared based on the latest pattern. We have provided class 11 Biology MCQs question with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
MCQ ON EPIDERMAL TISSUE SYSTEM is useful for NEET / CSIR / UGC / CBSE / ICSE / AIIMS / EXAM / AFMC EXAM / STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM/ KVS PGT BIOLOGY / NVS PGT BIOLOGY EXAM 2023-2024 ,2025
MCQ ON EPIDERMAL TISSUE SYSTEM / EPIDERMAL TISSUE SYSTEM class 11 for NEET
INTRODUCTION:-
EPIDERMAL TISSUE SYSTEM :-
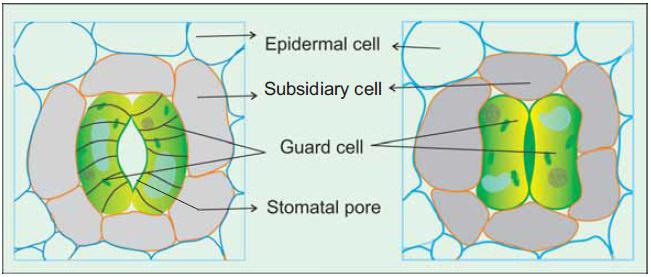
THE EPIDERMAL TISSUE SYSTEM forms the outermost covering of the whole plant body and comprises epidermal cells stomata and the epidermal appendages the trichomes and hairs.
The epidermis is the outermost layer of the primary plant body. It is made up of elongated compactly arranged cells which form a continuous layer. Epidermis is usually single layered. Epidermal cells are parenchymatous with a small amount of cytoplasm lining the cell
wall and a large vacuole.
The outside of the epidermis is often covered with a thick layer called the cuticle which prevents the loss of water.
Cuticle is absent in roots.
Stomata aur structures present in epidermis of the leaves.
Stomata regulate the process of transpiration and gases exchange. Each stoma composed of two bean shaped cells known as guard cells.
Guard cells possess chloroplast and regulate theopening and closing of stomata
THE COMPLEX TISSUES ARE MADE OF MORE THAN ONE TYPE OF CELLS.
THIS WORK TOGETHER IS A UNIT.
Xylum and phloem constituent the complex tissues in plants.
. PHLOEM :- PHLOEM transports food materials, usually from leaves to other parts of the plants. Phloem in angiosperm is composed of Sieve tube elements, companian cells, phloem parenchyma, and phloem fibres.
Gymnosperms have albuminous cells and sieve cells .They lacks sieve tubes and companion cells.
Sieve tubes elements are also long tube like structures arranged longitudinally and are sieve – like manner to form the sieve plates.
Companion cells :- The companion cells are specialised parenchymatous cells which are closely associated with sieve tubes elements.
PHLOEM Parenchyma :- It is made up of elongated tapering cylindrical cells which have dense cytoplasm and nucleus.
PHLOEM fibers:- it is made up of sclerenchymatous cells.There are generally absent in the primary phloem but are found in the secondary phloem.
XYLEM:-
XYLEM FUNCTION is a conducting tissue for water and minerals from roots to the stem and leaves . It also provides mechanical strength to the plants.
It is composed of four different kinds of elements , tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres , xylem parenchyma.
Gymnosperms lacks vessels in their xylem.
Tracheids are elongated or tube like cells with thick and lignified walls and tapering ends.
These are dead and are without protoplasm.The inner layers of cell walls have thickening which vary in form.
Vessel is along cylindrical tube like structure made of many cells called vessels members each with lignified walls and a large central cavity.
Xylem fibers have highly thickened walls and obliterated central lumens.
XYLEM parenchyma cells are living and thin walled and their cell walls are made up of cellulose.
They store food materials in the form of starch or fat .
The cells of the permanent tissues do not generally divide further. Permanent tissue having all cells similar in structure and functions are called simple tissues.
Permanent tissues having many different types of cells are called complex tissues.
Simple tissues:-a simple tissue is made of only one type of cells. The various simple tissues in plants are parenchyma, collenchyma and Sclerenchyma.
Parenchyma forms the major component within organs. The cells of the parenchyma are generally isodiametric.
They may be spherical , oval , round ,polygonal or elongated in shape.
Their walls are thin and made of cellulose.
They may either be closely packed or have small intercellular spaces.
The Parenchyma performs various functions like photosynthesis storage and secretion.
Collenchyma:-the Collenchyma occurs in layers below the epidermis in dicotyledonous plants.
It is found either as a homogeneous layer or patches.It consist of cells which are much thickened at the corners due to deposition of cellulose , hemicellulose and pectin.
Sclerenchyma:- it consist of long narrow cells with thick and lignified cell walls having a few or numerous pits.They are usually dead and without protoplasts.
MCQ EPIDERMAL TISSUE SYSTEM class 11 for NEET/KVS PGT BIOLOGY / NVS PGT BIOLOGY EXAM 2023-2024,2025
1. The outermost layer of the primary plant body
(a) epidemis
(b) endodemis
(c) parenchyma
(d) collenchyma
Ans (a) epidemis
2. The stomatal apparatus is made up of
(a) tracheids, vessels , xylem parenchyma , xylem fibres
(b) tracheids, protoxylem, metaxylem , vessels
(c) stomatal aperture , guard cells , subsidiary cells
(d) sieve tube elements , companion cells , phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres.
Ans. (c) stomatal aperture , guard cells and subsidiary cells
3. The outside of the epidermis is often covered with waxy thick layer called
(a) albuminous cells
(b) cuticle
(c) both a and b
(d) sieve tubes
Ans. (b) cuticle
4. Cuticle is absent in
(a) epidermis
(b) root
(c) stem
(d) leaf
Ans.(b) root
5. The structures present in epidermis of leaves
(a) stomata
(b) cuticle
(c) epidermis
(d) sieve tubes elements
Ans.(a) stomata
6. It regulates the process of transpiration and gaseous exchange.
(a) companion cells
(b) phloem fibres
(c) stomata
(d) phloem parenchyma
Ans.(c) stomata
7. Which stomach composed of two bean shaped cells known as
(a) companion cells
(b) guard cells
(c) xylem fibers
(d) tracheids
Ans.(b) guard cells
8. Ine grasses the guard cells are
(a) dumb – bell shaped
(b) xylem fibres
(c) pit fields
(d) circular shape
Ans.(a) dumb – bell shaped
9. The cells causes chloroplast and regulate opening and closing of stomata
(a) parenchyma
(b) Collenchyma
(c) guard cells
(d) companion cells
Ans. (c) guard cells
10.Sometimes a few epidermal cells , in the victinity of the guard cells become specialised in their shape and size are known as
(a) parenchymatous cells
(b) collenchyma
(c) phloem parenchyma
(d) subsidiary cells
Ans. (d) subsidiary cells
11.The cells of epidermis bear a ……
(a) parenchyma
(b) number of hairs
(c) phloem parenchyma
(d) phloem
Ans.(b) number of hairs
12…………..are unicellular elongation of the epidemal cells and help absorb water and mineral from the soil.
a) monocotyledonous
b) dicotyledonous
c) root hairs
(d) xylem parenchyma
Ans . (c) root hairs
13. On the stem the epidemal hairs are called
(a) sclerenchymatous cells
(b) tracheids
(c) trichomes
(d) endarch
Ans.(c) trichomes
14.The trichomes in the shoot system are usually ……
(a) unicellular
(b) protoxylem
(c) multicellular
(d) parenchyma
Ans. (c) multicellular
ALSO READ:-
● YOU CAN WATCH BIOLOGY SIR Youtube channel
15.Which tissue help in preventing water loss due to transpiration ?
(a) phloem fibres.
(b) endarch
(c) Collenchyma
(d) Trichomes
Ans.(d) trichomes
16.Epidermis are
(a) Collenchyma
(b) parenchymatous cells
(c) sclereids
(d) protophloem
Ans.(b) parenchymatous cells







Leave a Comment