MCQ ON Stamen microsporangium and pollen grain for NEET |MCQ ON Stamen microsporangium and pollen grain NEET Biology class 12 th |MCQ Questions for class 12 Biology chapter 2, Sexual reproduction in flowering plants with answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 12 Biology chapter 2 based on Stamen microsporangium and pollen grain with answers.
MCQ Questions for class 12 Biology with Answers were prepared based on the latest pattern. We have provided class 12 Biology MCQ questions on Stamen microsporangium and pollen grain with answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Stamen microsporangium and pollen grain
MCQ on is useful for NEET/ CSIR/ UGC/ CBSE/ ICSE /AIIMS EXAM/ AFMC EXAM/ JAC exam/ STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM
Introduction;-
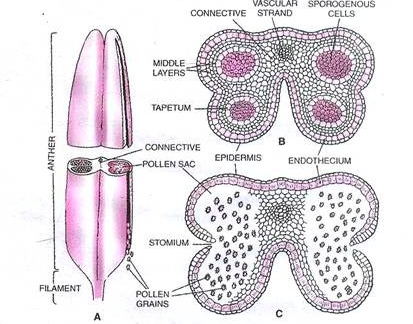
Stamen microsporangium and pollen grain:- The terms “stamen,” “microsporangium,” and “pollen grain” are all related to the male reproductive structures in flowering plants (angiosperms).
1. Stamen: The stamen is one of the two main parts of a flower’s reproductive system, the other being the pistil. The stamen is the male reproductive organ and consists of two primary components:
Anther: The anther is the top part of the stamen. It contains microsporangia, which are small structures where pollen grains develop. The anther is responsible for producing and releasing pollen.
1. Filament: The filament is the slender stalk that supports the anther and positions it above the flower’s female reproductive structure, the pistil. It acts like a pedestal for the anther.
2. Microsporangium: A microsporangium is a structure found within the anther of a stamen. It is essentially a pollen sac or chamber where microspore mother cells (also called pollen mother cells) undergo meiosis to produce microspores. These microspores are the precursors to pollen grains. Microsporangia contain the male reproductive cells and are responsible for the formation of pollen.
3.Pollen Grain: A pollen grain is a tiny, typically spherical structure produced within the microsporangium of the anther. Each pollen grain contains two cells: a generative cell and a tube cell. The generative cell is responsible for fertilization, as it divides to form two sperm cells. The tube cell plays a critical role in the pollination process. Once pollen is released from the anther, it can be transported to the stigma of a compatible flower, where it will germinate. The tube cell extends a pollen tube down through the style and into the ovary to deliver the sperm cells to the ovule, where fertilization occurs.
In summary, the stamen is the male reproductive structure in a flower, and within the stamen, the anther contains microsporangia, which produce pollen grains. Pollen grains are the male gametophytes of flowering plants and carry the male reproductive cells needed for fertilization when they reach the female reproductive structures of another flower.
MCQ ON Stamen microsporangium and pollen grain for NEET
Here are 15 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) related to stamen, microsporangium, and pollen grains, along with their answers:
1. What is the primary function of the stamen in a flower?
A) Photosynthesis
B) Reproduction
C) Support
D) Protection
Answer: B) Reproduction
2. Where are microsporangia typically located in a flower?
A) Petals
B) Sepals
C) Stamen
D) Pistil
Answer: C) Stamen
3. What is the main product of microsporangia in a flower?
A) Nectar
B) Pollen grains
C) Ovules
D) Seeds
Answer: B) Pollen grains
4. Which part of the stamen produces pollen?
A) Anther
B) Filament
C) Style
D) Ovary
Answer: A) Anther
5. What is the function of the filament in a stamen?
A) Producing pollen
B) Supporting the anther
C) Receiving pollen
D) Fertilizing the ovule
Answer: B) Supporting the anther
6. What is the primary purpose of pollen grains?
A) Attracting pollinators
B) Storing nutrients
C) Carrying genetic material
D) Protecting the ovules
Answer: C) Carrying genetic material
7. How are pollen grains typically dispersed from one flower to another?
A) Wind
B) Rain
C) Gravity
D) Insects
Answer: A) Wind
8. Which of the following is not a part of the male reproductive structure in a flower?
A) Anther
B) Stigma
C) Filament
D) Pollen grain
Answer: B) Stigma
9. Where does pollen land during pollination to complete fertilization?
A) Anther
B) Filament
C) Stigma
D) Ovary
Answer: C) Stigma
10. What is the term for the process of pollen transfer from anther to stigma?
A) Fertilization
B) Germination
C) Pollination
D) Reproduction
Answer: C) Pollination
11. What is the mature, fertilized structure that develops from the ovule?
A) Pollen grain
B) Stamen
C) Seed
D) Ovary
Answer: C) Seed
12. What is the main purpose of pollen tube growth after pollination?
A) Attracting pollinators
B) Protecting the ovule
C) Delivering sperm cells to the ovule
D) Storing nutrients
Answer: C) Delivering sperm cells to the ovule
13. In gymnosperms, where are the microsporangia typically located?
A) In the ovules
B) On the leaves
C) In cones
D) In the petals
Answer: C) In cones
14. What is the outer layer of a pollen grain called?
A) Exine
B) Intine
C) Cytoplasm
D) Nucleus
Answer: A) Exine
15. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of gymnosperms’ pollen grains?
A) Encased in a protective coating
B) Produced in cones
C) Typically carried by wind
D) Fertilized by insects
Answer: D) Fertilized by insects
Conclusion:-
MCQ ON Stamen microsporangium and pollen grain for NEET |:-What is the outer layer of a pollen grain called?, A) Exine, B) Intine, C) Cytoplasm, D) Nucleus, Answer: A) Exine







Leave a Comment