|MCQMCQ ON Sexual reproduction in flowering plants for NEET ON Sexual reproduction in flowering plants NEET Biology class 12th |MCQ Questions for class 12 Biology chapter 2, Sexual reproduction in flowering plants with answer | Check the below NCERT MCQ question for class 12 Biology chapter 2 based on Sexual reproduction in flowering plants with answers.
MCQ Questions for class 12 Biology with Answers were prepared based on the latest pattern. We have provided class 12 Biology MCQ questions on Sexual reproduction in flowering plants with answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants
MCQ on is useful for NEET/ CSIR/ UGC/ CBSE/ ICSE /AIIMS EXAM/ AFMC EXAM/ JAC exam/ STATE LEVEL MEDICAL EXAM
Introduction:-
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants:- Sexual reproduction in flowering plants, also known as angiosperms, is a process by which new plants are produced through the fusion of specialized reproductive cells called gametes. This process involves several key steps and structures:
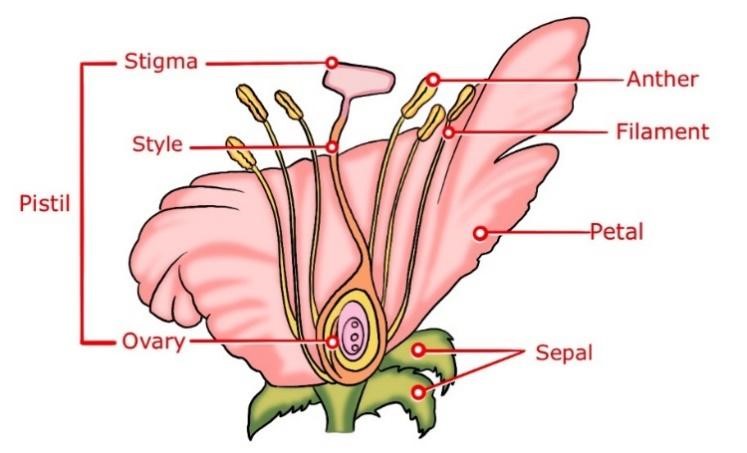
1.Flower Formation: The reproductive process in flowering plants begins with the development of flowers. Flowers are complex structures that serve as the reproductive organs of the plant. They typically consist of four main parts: sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils.
2. Male and Female Parts: Within a flower, there are male and female reproductive organs. The male reproductive organ is called the stamen, which includes anther and filament. The female reproductive organ is called the pistil, which consists of the stigma, style, and ovary.
3. Pollen Production: In the anther of the stamen, pollen grains are produced. Pollen grains contain the male gametes or sperm cells of the plant.
4. Ovule Formation: Inside the ovary of the pistil, ovules develop. Each ovule contains the female gametes or egg cells of the plant.
5. Pollination: The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination. This can occur through various mechanisms, including wind, water, animals (such as bees and butterflies), or even self-pollination within the same flower.
6. Fertilization: Once pollen lands on the stigma, it produces a pollen tube that grows down through the style and enters the ovary. The male gametes (sperm cells) then travel down the pollen tube to reach the female gametes (egg cells) within the ovule. Fertilization occurs when one sperm cell fuses with an egg cell, forming a zygote.
7. Seed Formation: The zygote, which is now a fertilized egg, develops into an embryo within the ovule. This embryo will eventually become a new plant. The ovule matures into a seed, which contains the embryo, along with stored nutrients and a protective seed coat.
8. Fruit Development: In many cases, the ovary of the flower swells and develops into a fruit. The fruit protects the seeds and aids in their dispersal. Animals may eat the fruit and disperse the seeds, helping the plant spread to new locations.
9. Seed Dispersal: Once mature, the fruit releases or disperses its seeds, allowing them to germinate and grow into new plants, thus completing the life cycle.
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants promotes genetic diversity and adaptability within plant populations. It allows for the creation of unique combinations of traits by combining genetic material from different parent plants. This diversity is essential for the survival and evolution of plant species in changing environments.
MCQ ON Sexual reproduction in flowering plants for NEET
Here are 15 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) related to sexual reproduction in flowering plants, along with their answers:
1. What is the primary purpose of flowers in flowering plants?
a) To provide shade
b) To photosynthesize
c) To serve as reproductive organs
d) To store water
Answer: c) To serve as reproductive organs
2. Which part of the flower contains the male reproductive organs?
a) Sepals
b) Petals
c) Pistil
d) Stamens
Answer: d) Stamens
3. What is the female reproductive organ in a flower?
a) Petals
b) Stamens
c) Pistil
d) Sepals
Answer: c) Pistil
4. What do pollen grains contain?
a) Female gametes
b) Male gametes
c) Ovules
d) Seeds
Answer: b) Male gametes
5. How is pollination typically achieved in many flowering plants?
a) Through self-pollination within the same flower
b) Through photosynthesis
c) Through asexual reproduction
d) Through seed dispersal
Answer: a) Through self-pollination within the same flower
6. What part of the flower receives pollen during pollination?
a) Ovary
b) Stigma
c) Anther
d) Filament
Answer: b) Stigma
7. What is the outcome of successful fertilization in a flowering plant?
a) Formation of a fruit
b) Formation of a new flower
c) Formation of a leaf
d) Formation of a root
Answer: a) Formation of a fruit
8. What is the term for the transfer of pollen from one flower to another flower of the same plant?
a) Cross-pollination
b) Self-pollination
c) Wind pollination
d) Insect pollination
Answer: b) Self-pollination
9. In cross-pollination, how is pollen typically transferred between flowers?
a) By wind
b) By water
c) By animals, such as bees or butterflies
d) By gravity
Answer: c) By animals, such as bees or butterflies
10. Where are female gametes (egg cells) found in a flowering plant?
a) In the anther
b) In the filament
c) In the ovules within the ovary
d) In the stigma
Answer: c) In the ovules within the ovary
11. What is the result of fertilization in a flowering plant?
a) Formation of a zygote
b) Formation of pollen grains
c) Formation of a new flower
d) Formation of a seed
Answer: d) Formation of a seed
12. What is the purpose of the fruit in a flowering plant?
a) To protect the flower
b) To store water
c) To disperse the seeds
d) To photosynthesize
Answer: c) To disperse the seeds
13. Which of the following is NOT involved in sexual reproduction in flowering plants?
a) Stamens
b) Stigma
c) Sepals
d) Ovules
Answer: c) Sepals
14. How does sexual reproduction in flowering plants contribute to genetic diversity?
a) By producing genetically identical offspring
b) By combining genetic material from two different plants
c) By preventing fertilization
d) By producing haploid offspring
Answer: b) By combining genetic material from two different plants
15. What is the term for the process by which a seed starts to grow and develop into a new plant?
a) Fertilization
b) Pollination
c) Germination
d) Photosynthesis
Answer: c) Germination
Conclusion:-
MCQ ON Sexual reproduction in flowering plants for NEET | What do pollen grains contain?, a) Female gametes, b) Male gametes, c) Ovules, d) Seeds, Answer: b) Male gametes.







Leave a Comment