Budding in Hydra, Yeast, Scypha and Spongilla with diagram, Hi guys in this article we know about what is budding,its types, mechanism and occurrence. We read about budding in hydra, Yeast, Scypha and gemmule formation in freshwater sponge spongilla.
Budding is type of Asexual mode of reproduction in which one or more unicellular or multicellular outgrowth called, buds are formed on or inside the parent body. Each multicellular outgrowth called bud enlarge, develop the parental characters and then separate to lead an independent life, it feeds, grows and become an adult and repeat the process.
★ WATCH THIS VIDEO
Budding is found in a sponge (Scypha, spongilla),coelenterates ( Hydra), annelids and among fungi, it is found in Yeast.
◆ Follow me on YouTube
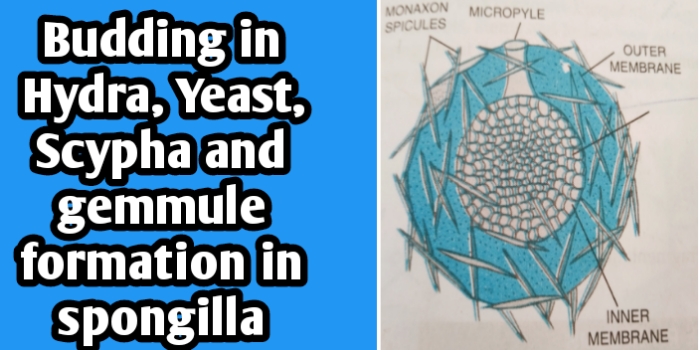
According to presence inside or outside the body budding is two types 1) Exogenous and 2) Endogenous. In Exogenous budding, bud is present outer surface of the parent body, it is found in Hydra and Scypha. Endogenous budding bud is present inside of parent body, it is found in a freshwater sponge name as Spongilla. A number of endogenous buds called gemmules are formed inside the Spongilla parental body.
Budding in Hydra, Yeast and Spongilla with diagram
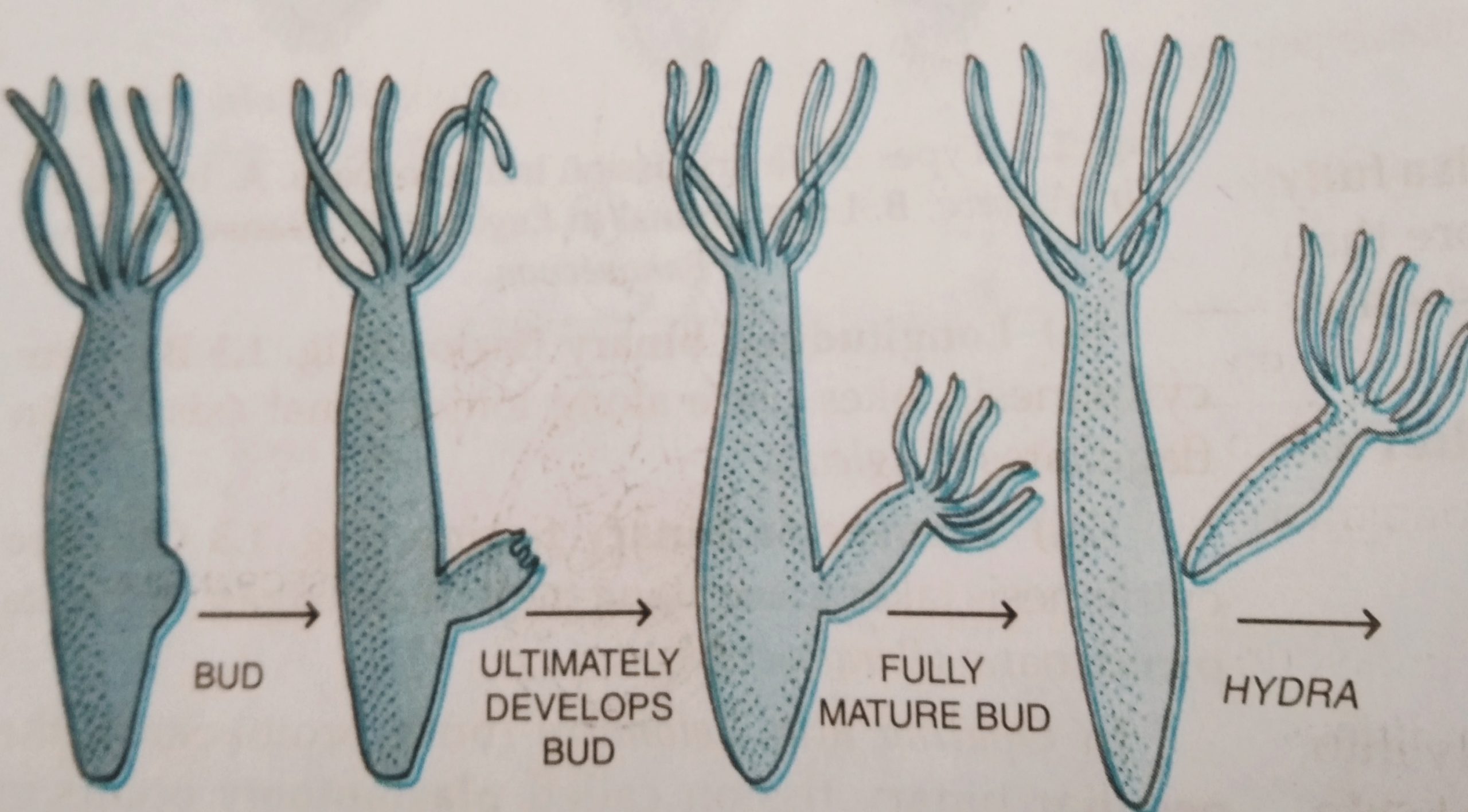
Budding in Hydra with diagram:- Organisms such as hydra use regenerative cells for reproduction in the process of budding. In hydra, a bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at one specific site. These buds develop into tiny individuals and, when fully mature, detach from the parent body and become new independent individuals. Now look at the picture budding in hydra with diagram
Budding in Yeast with diagram:- Yeasts are non-green, eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms belonging to the kingdom fungus. They are generally larger than the bacteria and they typically measure 3-4 µm in diameter. Yeast cells reproduce asexually by an asymmetric division process called budding.
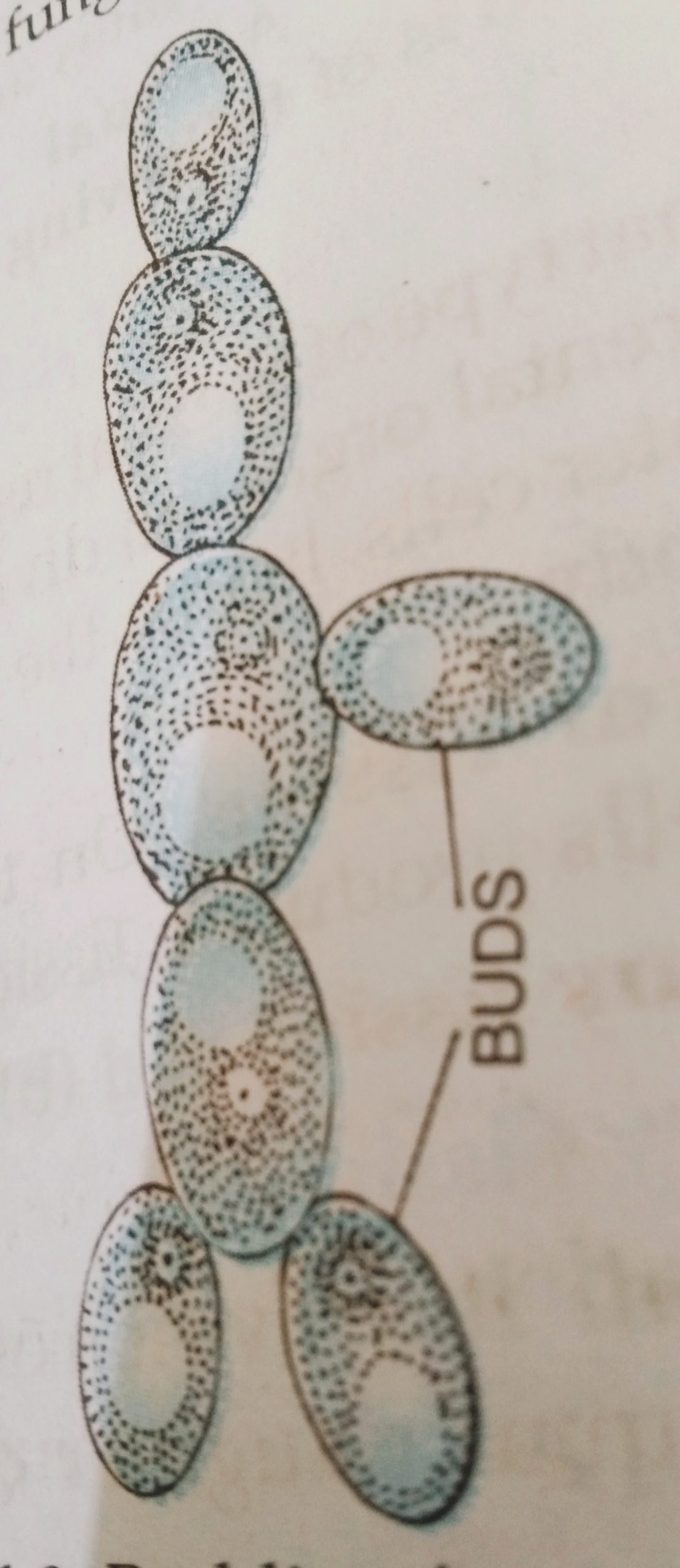
Budding in Yeast with diagram
In yeast, budding usually occurs during the abundant supply of nutrition. In this process of reproduction, a small bud arises as an outgrowth of the parent body. Later the nucleus of the parent yeast is separated into two parts and one of the nuclei shifts into the bud. The newly created bud divides and grows into a new cell.
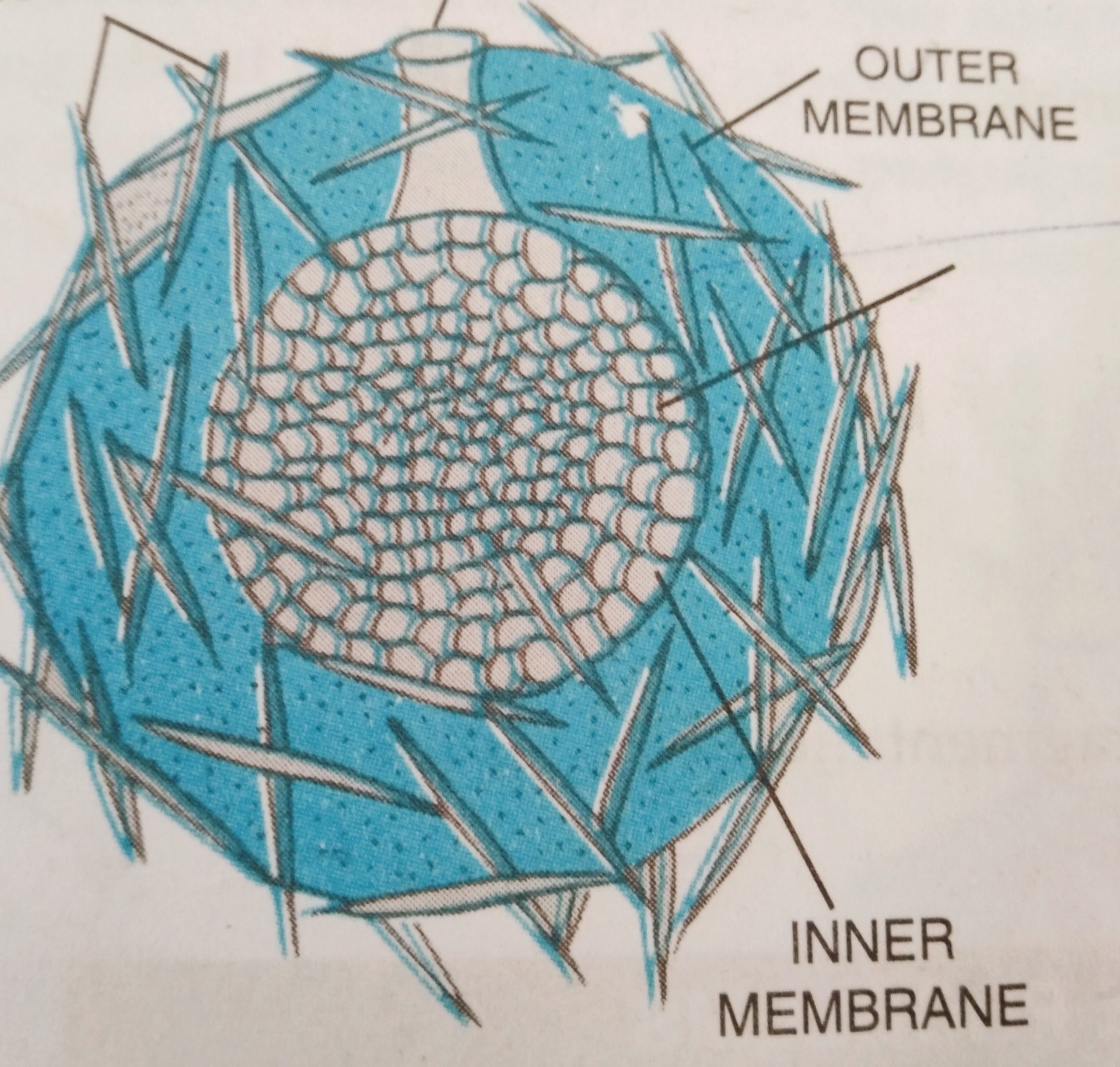
Gemmules formation in Spongilla
Gemmules formation in Spongilla: Spongilla a freshwater sponge the bud is endogenous as number of bud called gemmule are formed inside the parental body. Is gemmule of spongilla is mass of undifferentiated cells called archaeocytes, surrounded by a protective coat of amphidisk spicules. Gemmule helps in perennation and dispersal. During favourable condition archaeocytes come out of gemmule through micropyle and form an new sponge.


Leave a Comment